We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
18 Nutrients to Boost Fertility in Men and Women

Table of Contents
For millions of people, the road to parenthood is a major challenge, and evidence suggests that it’s getting harder.
Up to 15% of couples are affected by infertility. And fertility specialists like Shanna Swan, foresee that most couples may need assisted reproduction by 2045.
The good news is that nature has gifted us numerous nutrients proven to boost fertility in both men and women.
Here are 18 of the most important nutrients that you can get simply by eating a fertility diet rich in high-quality superfoods.
1. Fat Boosts Fertility
Fat is the key nutrient to boost fertility. It’s an essential building block for our cells and helps synthesize vital reproductive hormones.
Dietary fat provides our bodies with energy and essential fatty acids that it can’t produce on its own. Fatty acids from animal sources assist with blood clotting and increase brain function.
Fat also enables the body to absorb essential vitamins like A, D, and E, which all increase fertility.
Though each of these functions is crucial, the most important benefit of eating fat for fertility is that it helps to reduce inflammation by arresting the activity of harmful cells that trigger the immune responses that cause inflammation.
Natural fats from high-fat meats like ribeye, pork belly, ribs, fatty fish, and full-fat dairy products like butter and cream, lubricate the lymphatics while filtering out harmful pathogens.
2. Vitamin A
The vitamin A we get from foods like eggs and fatty fish is a fertility supernutrient. It improves egg quality, ovarian response, implantation, embryonic development, and placental formation.
Vitamin A also plays a role in immune function, reproduction, and cell communication.
The vitamin A we get from animal foods, especially when combined with healthy fats is far more bioavailable than the vitamin A we get from plants like carrots.
In fact the beta-carotene in carrots is really a precursor to vitamin A that your body needs to convert into truly useable vitamin A.
3. Vitamin D
Vitamin D is produced by the body in response to exposure to the sun, and we also get it from foods like full-fat dairy. But for most people getting enough vitamin D is difficult without supplementation, especially during the winter months.
Developing babies receive calcium and vitamin D from the mother during pregnancy, so it’s important to ensure that both mom and baby have adequate levels of both.
Vitamin D deficiency in mothers can contribute to the development of childhood rickets and long-term health problems like type 1 diabetes.
Research has shown that most women require vitamin D supplementation to ensure adequate maternal vitamin D levels.
Studies also show that vitamin D supplementation can have a positive impact on pregnancy rates and fertility treatment outcomes. In one study, women with adequate levels of vitamin D had a 52.5% chance of pregnancy per IVF cycle compared to women with insufficient levels only having a 34.7% chance. The women with adequate vitamin D levels also had higher implantation rates.
4. Folate
Folate, also known as B9, plays a role in cell growth and development. Specifically, folate is required for building DNA and for proper cell division.
It’s recommended that all women who are trying or planning to get pregnant take folate to prevent neural birth defects. Trials have shown that women with higher levels of folate had higher live birth rates in comparison to women with lower folate levels.
Studies have also shown that folate can improve oocyte counts and embryo quality in couples undergoing fertility treatment.
One study following 232 women undergoing fertility treatment showed that higher folate intake was associated with higher rates of implantation, clinical pregnancy, and live birth.
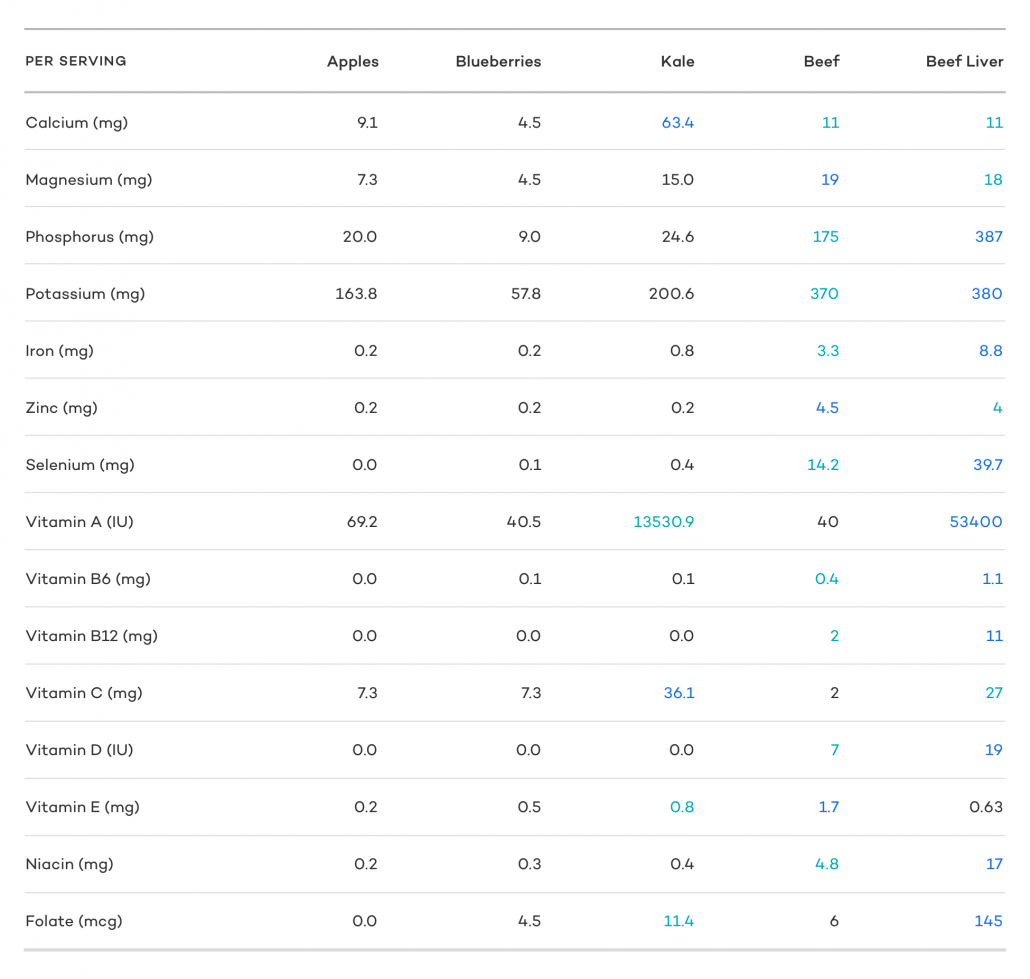
Folate in adequate amounts is usually hard to come by through food sources alone. While dark leafy greens are lionized for their folate content by mainstream nutritionists, as you can see in the chart above, beef liver and other animal-based foods will ensure you get all you need.
5. Zinc
Low levels of zinc are associated with erectile dysfunction and lower sperm count in males. So if you’re aim is to boost fertility, upping your zinc intake is a good place to start.
The good news is that the zinc found in meat is 400% more bioavailable than zinc found in breakfast cereals.
This exceptional bioavailability, when compared with zinc in plant foods, is due to the presence of plant phytates that interfere with absorption.
Studies show that vegan and vegetarians have low zinc levels, and lower levels when compared to meat-eaters.
Other studies show that zinc deficiency affects motor and cognitive development in children.
Zinc also protects against coronary artery disease, is essential in insulin formation, and has been shown to increase glycemic control for diabetics.
6. Heme Iron

Heme iron is only found in red meat and plays a major role in many of the physiological functions critical for wellbeing and fertility.
Iron is an essential mineral for growth, development, and the production of hormones. The body uses it to make hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to organs and tissues throughout the body, and myoglobin, a protein that provides oxygen to muscles.
The amount of blood in a woman’s body increases by 30-50% during pregnancy. Extra iron is necessary to support the increased blood volume.
Iron deficiency is believed to factor in babies being born undersized or prematurely. Research has also shown that iron levels are related to a woman’s risk of ovulatory infertility.
One study showed that women who consumed iron supplements had a significantly lower risk of ovulatory infertility compared to women who did not use iron supplements.
Iron also plays a key role in immune function, is essential to cognition, and participates in energy metabolism. A wide-ranging 2016 review found significant deficiencies for vegans and vegetarians with women being particularly susceptible to low iron anemia.
7. Omega-3

Found in abundance in fatty fish, omega-3s can boost fertility by improving sperm motility, while helping women achieve pregnancy and supporting healthy fetal development.
Two large studies found that women consuming 600–800 mgs of an omega 3 called DHA daily during pregnancy reduced their risk of early preterm birth by more than 40% in the US and 64% in Australia.
Other studies have shown that omega 3s can improve ovulation, ovarian reserve, and overall fertility.
For men lacking in DHA, sperm health and motility are compromised, reducing a man’s fertility. It’s important to remember that 1/3 of infertility is exclusively male factor, and that male fertility issues factor into at least 50% of all infertility.
8. CoQ10 -Coenzyme Q
Co-Q10 helps generate energy in human cells. An increase of Co-Q10 in the blood has been shown to positively impact both female and male fertility.
A 2018 study found that pre-supplementation with Co-Q10 boosts fertility by improving ovarian response in women undergoing IVF treatment. Co-Q10 has also been shown to improve ovarian reserve, egg quality, and embryo quality.
Female fertility declines rapidly after women turn 40 due to a decrease in oocyte quality and quantity. A 2015 study showed that suboptimal levels of CoQ10 can lead to oocyte deficits and age-associated causes of infertility. The study showed evidence that supplementing Co-Q10 can reverse the age-related decline in oocyte quantity and quality.
Simply put, Co-Q10 helps combat age-related causes of infertility. And you can get it from your diet in the form of red meat and especially liver. It’s also a proven anti-fatigue factor, and has shown to increase sperm motility in men.
9. Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient vital to many body functions. Choline supports cell growth, metabolism, liver, and muscle function. The body naturally produces choline, but the majority comes from a diet rich in meat and eggs.
Fertility specialists are increasingly recognizing the importance of ensuring adequate levels of choline during pregnancy. Research has shown that choline plays several critical roles in the prenatal period including tissue expansion, brain-development, and neurotransmission.
Most pregnant women in the U.S. do not meet recommended levels of choline. Studies have shown that supplementing mother’s diets with additional choline improves pregnancy outcomes and protects against some neural and metabolic impairments.
10. Carnosine
One of the most promising anti-aging compounds, carnosine is found almost exclusively in meat. This powerful peptide exists throughout the body in areas of high energy use including the brain, heart, and muscles. It’s there to protect these critical areas from the ravages of energy production and management.
When we’re young we have high levels of carnosine in these energy-demanding tissues but as we age, our carnosine levels decline. Carnosine is effective at preventing glycation–the harmful bonding of glucose molecules to your cells and DNA. Antiglycation is synonymous with anti-aging and linked to reductions in the development of Alzheimers, renal disease, and atherosclerosis, and inflammatory conditions like PCOS that cause infertility.
Studies show that carnosine can boost fertility by increasing sperm mitochondrial activity. It can also prevent and repair testicular dysfunction and the recovery of spermatogenesis.
Carnosine is also a powerful antioxidant that destroys free radicals while reducing damage and shortening of telomeres–another powerful anti-aging property.
11. Carnitine
Carnitine is another compound found almost exclusively in red meat, and has been shown to play a significant role in improving male fertility.
Carnitine drives sperm metabolism by providing readily available energy used for motility and maturation. Research has shown that supplementing carnitine in the form of ACL can help to treat male fertility issues, especially those resulting from sperm motility issues.
Other studies show that supplementing l-carnitine can increase sperm motility and morphology.
12. Lysine

An amino acid found in beef and pork, Lysine can boost the body’s production of the growth hormone hGH, which is crucial for normal female fertility.
Low hGH is associated with infertility and conditions like PCOS. Lysine also helps blood sugar response, and can improve calcium absorption and retention.
13. Creatine
You’ve probably heard of creatine as a popular supplement with athletes and weightlifters, and it’s another compound only found in meat.
Studies have shown that when vegetarians add creatine supplements to their diets they show improved cognitive function.
Creatine has also been shown to improve athletic performance in both vegetarians and omnivores. Interestingly, Alzheimers patients show lower creatine levels.
When given to patients with heart failure, creatine has been shown to improve cardiovascular performance. For people with type 2 diabetes, supplementing with creatine combined with exercise improves glycemic control. Current research raises the possibility that improvements in maternal diet, or supplementation with creatine, could protect a baby from poor growth and even brain injury during a difficult birth process.
14. Taurine
Similar to carnosine, taurine is a powerful antioxidant that reduces glycation, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Taurine has been shown to have an anti-depressive effect in animal studies on depressive rats–poor critters. This effect suggests that taurine may be a factor in the sense of wellbeing that many people describe when eating meat, especially after periods of abstaining or scarcity.
New research suggests that increasing taurine in your diet can increase male fertility by improving overall sperm health. The study found that taurine production declines significantly with age. Increasing your taurine intake is shown to counteract any age-related decline in sperm quality.
15. Vitamin B12
AKA cobalamin, B12 is exclusive to animal products. Recent studies have found that up to 86 percent of vegan children, 90 percent of vegan elderly, and 62 percent of pregnant vegan women are B12 deficient.
Studies suggest that B12 deficiency can result in dementia and Alzheimers disease. In 2013 a high-quality randomized control trial found that supplementation of Vitamin B12 significantly improved depressive symptoms.
For woman trying to conceive, B12 deficiency will likely create difficulty, and a lack of vitamin B12 can lead to pregnancy complications, including low birth weight, spontaneous abortion, and neural tube defects.
Getting the right amount of B12 in your diet will protect you against these potential problems and may enhance fertility in women who are undergoing infertility treatment.
16. Selenium
Selenium is another mineral in short supply in most natural sources. Yet it’s vital to boost fertility, thyroid function, DNA production, and protecting the body from damage caused by free radicals.
Research shows that selenium promotes the growth of healthy follicles in the ovaries, which develop and release the eggs. As an antioxidant, selenium protects against birth defects and miscarriages caused by DNA damage.
Foods high in selenium include fish, pork, beef, and turkey.
17. Magnesium
Around 80% of Americans are magnesium deficient. A Western diet high in refined sugar depletes magnesium.
In a study of women’s health at Harvard following 17,000 women, those on a high carb diet had higher infertility rates than women who ate fewer sugars. In addition to reducing magnesium, high sugar intake leads to increased insulin resistance, often implicated in PCOS.
Magnesium-rich animal-based diets increase insulin sensitivity and ovulatory function.
When trying to conceive with IVF, a magnesium-rich diet can improve embryo transfer by lowering inflammation which increases chances of implantation.
Male infertility has also been associated with lower magnesium levels.
18. Copper
Copper plays an important role in nearly every body function. It’s critical for creating energy, maintaining blood vessels, and creating connective tissue.
Copper helps maintain the immune system, the nervous system, and activates genes. It is also critical for brain development. Studies show that copper deficiencies negatively impact fertility in women by disrupting normal estrogen metabolism.
How to Boost Fertility with Super Nutrients from your Diet
By now it should be clear that many of the nutrients you need to boost fertility are found exclusively and abundantly in animal-based whole foods.
A diet rich in high-quality animal fats and proteins will gift your body fertility boosting nutrients with every meal.
Eating to maximize your intake of healthy fats while cutting out carbs is the foundation of the fertility diet. And there are a number of variations that you can try including, the carnivore diet, the keto diet, and the Mediterranean keto diet.
The emphasis on animal-based foods is based on head-to-head comparisons with plant-based superfoods. As you can see, there’s no match for animal superfoods in nearly every meaningful nutritional category.