We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Top 6 Benefits of Red Meat

Red meat has many benefits thanks to an abundance of macro and micronutrients. Red meat provides complete proteins, healthy fats, B vitamins, and numerous meat-specific nutrients.
In fact, red meat is among the most nutrient-dense foods on earth.
Yet, since the 1950s, red meat has also been targeted by research aimed at linking it with heart disease and cancer. The good news is that despite the conflicting claims about the health effects of meat, modern research tells us that there is in fact, zero evidence that links eating fresh red meat to disease.
In this article, we’ll review the evidence-based benefits of red meat.
Table of Contents
What is Red Meat?
Red meat is the meat of mammals high in a protein called myoglobin. When myoglobin binds with oxygen, it gives meat a red color.
Examples of red meat include:
- beef
- veal
- pork
- lamb
- goat
- Bison
- Elk
- Venison
Is it Safe to Eat Red Meat: What Studies Say
Before detailing the benefits of red meat, let’s take a moment to address the stigma against red meat.
Though red meat has been targeted as a cause of disease since the 1950s, modern studies show that fresh red meat is, in fact, not associated with disease.
Red meat was first targeted for its saturated fat content. In the 1950s, a few influential scientists incorrectly linked saturated fat intake with heart disease.
It has taken more than half a century to set the record straight.
Numerous modern studies, including data from millions of participants, confirm that for the average person, saturated fat is not associated with heart disease, cancer, stroke, diabetes, and death from heart attack.

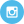
This bellwether 2020 study, co-authored by researchers from the world’s leading medical schools, concluded that consuming unprocessed red meat is not associated with heart disease.
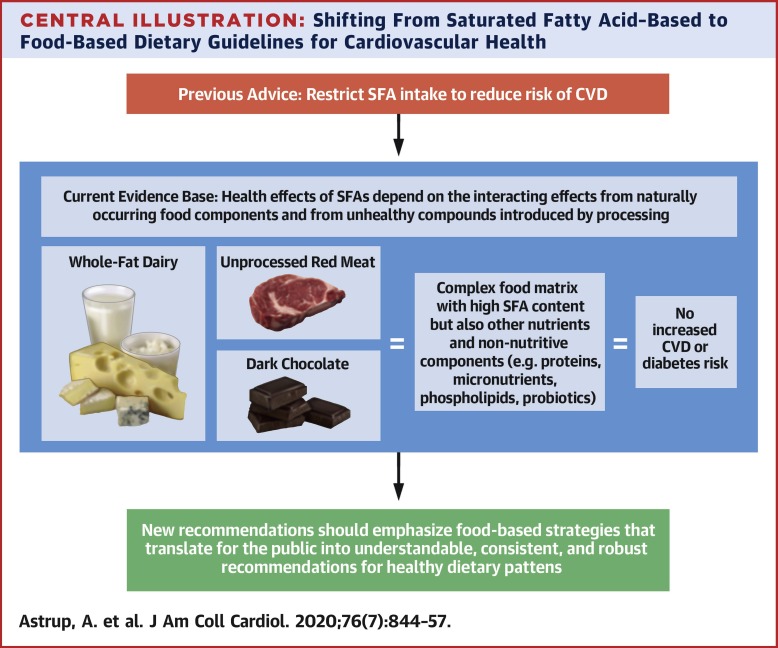
The authors stated, “Whole-fat dairy, unprocessed meat, and dark chocolate are SFA-rich foods with a complex matrix (of nutrients) that are not associated with an increased risk of CVD. The totality of available evidence does not support further limiting the intake of such foods.”
What about Cancer?
As with heart disease, there is no reliable evidence linking fresh red meat with cancer.
But this is not for lack of trying–there have been hundreds of studies attempting to make the link. For decades the suspicion itself was enough to convince health officials to recommend reducing meat intake.
But what does the science actually say?

In 2019 the NutriRECS study, most comprehensive research to date looked at data from 48 studies with over 5.7 million participants.
The researchers concluded that:
- organizations like the WHO that use observational studies for their recommendations do not issue rigorous reviews of the studies
- Reducing fresh red meat has no impact on incidences of prostate cancer mortality, as well as incidences of overall, breast, colorectal, esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, and prostate cancer
- Very weak evidence that processed meat is associated with a very small absolute risk reduction in overall lifetime cancer mortality; prostate cancer mortality; and the incidence of esophageal, colorectal, and breast cancer (range, 1 fewer to 8 fewer events per 1000 persons with a decrease of 3 servings/wk), with no statistically significant differences in incidence or mortality for 12 additional cancer outcomes (colorectal, gastric, and pancreatic cancer mortality; overall, endometrial, gastric, hepatic, small intestinal, oral, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer incidence)”
- Final Recommendations: Contrary to the WHO, the researchers recommend continuing to eat both fresh red meat and processed meats.
For an in-depth look at research on the questions of red meat and cancer, click here.
Top 6 Benefits of Red Meat
Over the decades, attempts to vilify red meat have distracted from its potent health benefits.
The numerous benefits of red meat can be attributed to its robust macro and micronutrient profile.
To explore the benefits of red meat, we’ll look both at studies showing the health effects of eating meat on a population level, as well as the benefits of specific nutrients found in abundance in red meat.
1 Red Meat is Loaded with Healthy Fats
Red meat provides a complex of healthy fats, including saturated fat, monounsaturated fat, omega-3 fatty acids, and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA).
Let’s look at how the fats in red meat can benefit your health:
- monounsaturated fat has proven anti-inflammatory properties and has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease
- The balance of saturated and unsaturated fats in red meat is essential to your bodies ability to create and maintain healthy cell membranes
- Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) supports immune function and heart health, strengthens bones, reduces excess body fat, and has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of various cancers
- Omega-3 fatty acids in red meat like lamb can be found in levels as high as salmon. Omega-3s play an important role in numerous physiological functions like male and female fertility and form the basis of hormones that regulate blood clotting and the health of your arterial walls
- Stearic acid, one of the most common saturated fats in red meat, has been shown to improve weight loss, support mitochondrial function, and shows no evidence of contributing to heart disease.
On the other hand, numerous studies have shown that substituting animal fats with industrial vegetable oils has resulted in increased risks of inflammation, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and various cancers.
2 Eating Meat is Associated with Longevity
A study of more than 218,000 people from over 50 countries shows that consuming unprocessed meat regularly can reduce the risk of early death while increasing longevity.

These findings are independent of total caloric intake, economic status, urban advantages, and obesity.
Furthermore, Hong Kong, the country with the greatest total meat consumption and 3rd highest level of red meat consumption, also has the world’s longest life expectancy at 84.5 years.
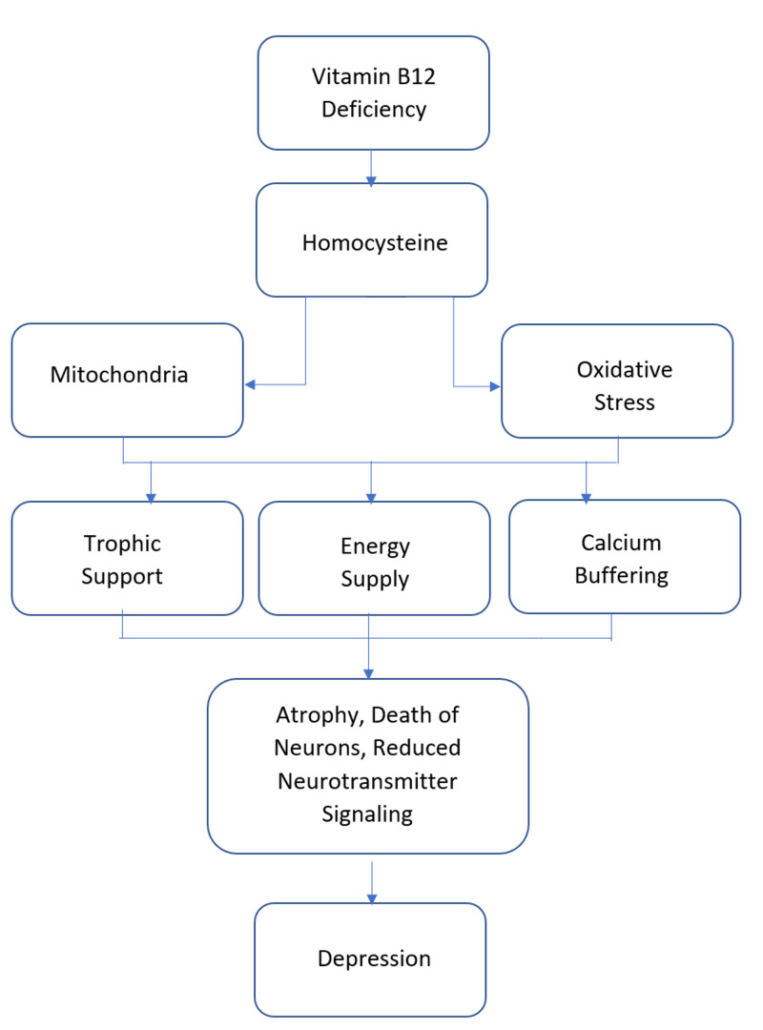
3 Red Meat Supports Mental Health, Reduces Risk of Depression
Numerous studies link eating red meat with improvements in mental health and reductions in symptoms of depression.
On the other hand, vegan and vegetarian diets are linked with psychiatric disorders and a significantly greater likelihood of depression.
In 2014, Austrian researchers published a study that included 330 vegetarians, 330 people who consumed a lot of red meat, 330 omnivores who ate less meat, and 330 people who consumed a little meat but ate mostly fruits and veggies.
The subjects were matched for sex, age, and socio-economic status. Researchers found that vegetarians were twice as likely as the other groups to suffer from a mental illness such as anxiety and depression.
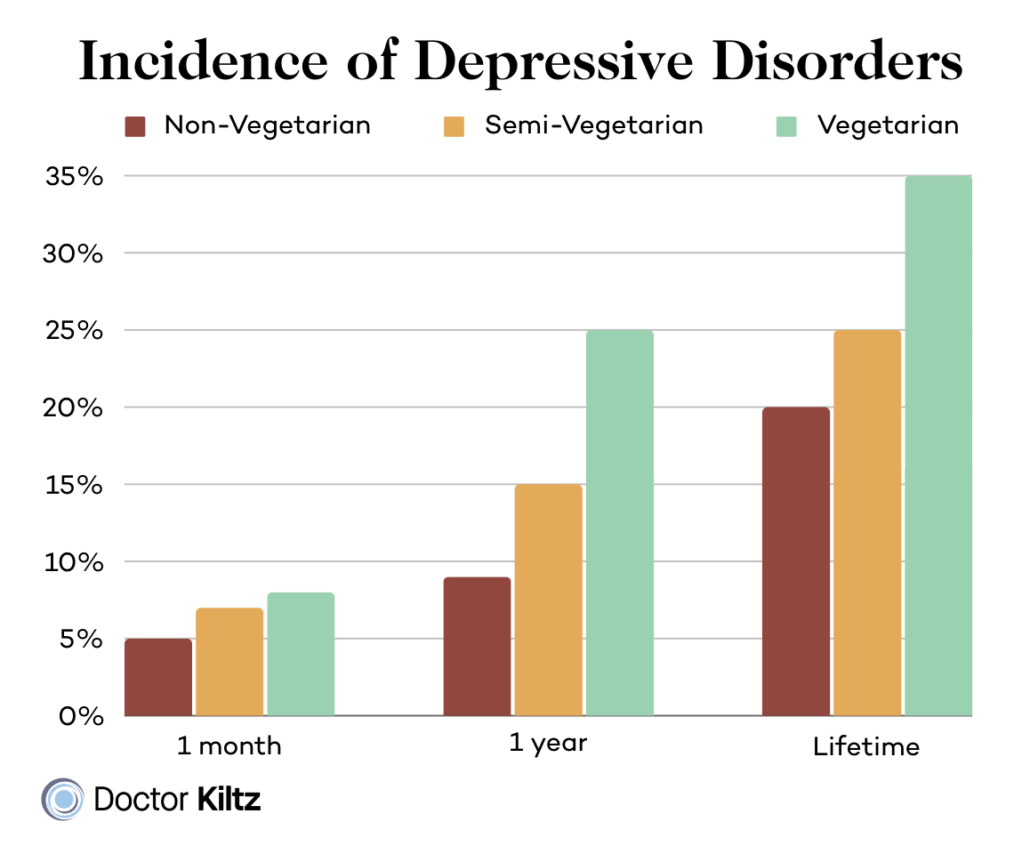
Though the study above didn’t identify a specific reason for meat’s benefits on mental health, it is likely do to the many nutrients that you find only, or mostly in meat.
For example, studies tell us that vitamin B12 and creatine–both found in high amounts in red meat–play a significant role in the reduction of depression.

Studies show that B12 figures in numerous physiological and neurochemical pathways to support stable mood and mental health.
In a 2018 French study of 90,000 adults, researchers looked at the impact that giving up various food groups had on depressive symptoms.
The researchers found that incidences of depression increased with each food group that was given up. These included red meat, poultry, fish, and dairy. Participants who had given up at least three of four animal-based food groups had a nearly 250% greater risk of depression.
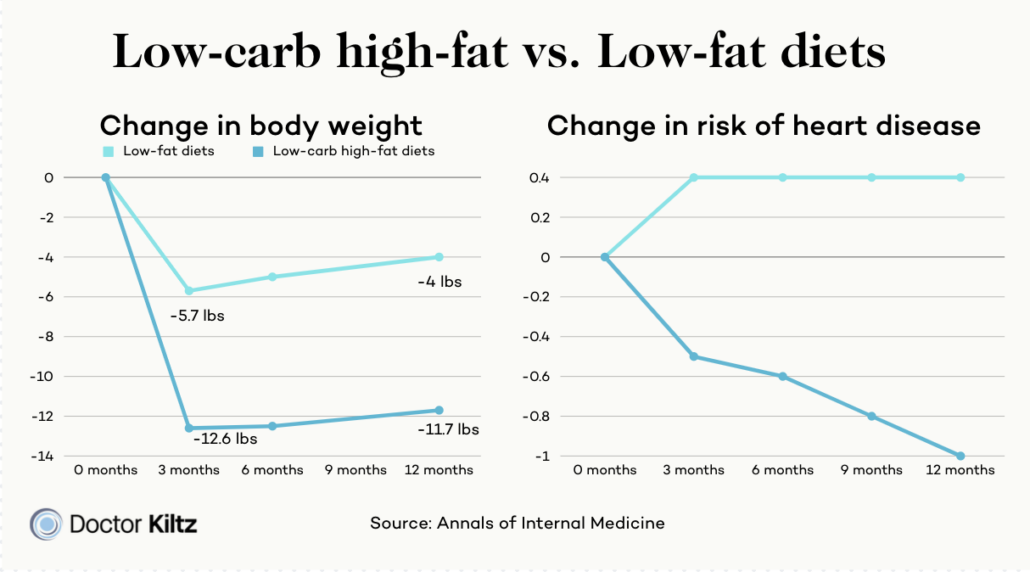
4 Better outcomes from High-Meat Low-Carb vs. Non-Meat Diets
When looking at the few quality randomized control trials comparing low-carb diets high in red meat to non-meat diets, the high meat diets showed dramatically better outcomes regarding cardiovascular health and weight loss.
5 All Meat (Carnivore) Diets High In Red Meat Show Numerous Benefits
Recent studies on ancestral eating enthusiasts practicing an all-meat carnivore diet have shown remarkably positive benefits.
A 2021 study by Harvard University researchers Dr. Belinda Lennerz and Dr. David Ludwig gathered data from 2,029 carnivore dieters over 6 months.
The researchers concluded: “Contrary to common expectations, adults consuming a carnivore diet experienced few adverse effects and instead reported health benefits and high satisfaction.”

Significant health benefits included:
- 93% improved or resolved obesity and excess weight
- 93% improved hypertension
- 98% improved conditions related to diabetes
- 97% improved gastrointestinal symptoms
- 96% improved psychiatric symptoms
Similar to the Harvard study above, the Revero carnivore-based health program founded by Dr. Shawn Baker found similarly robust health benefits, including widespread symptom reversals and medication terminations.
In fact, 79% of survey participants eliminated or reduced all medications after 3 months.
6 Numerous Nutrients Found Only in Red Meat
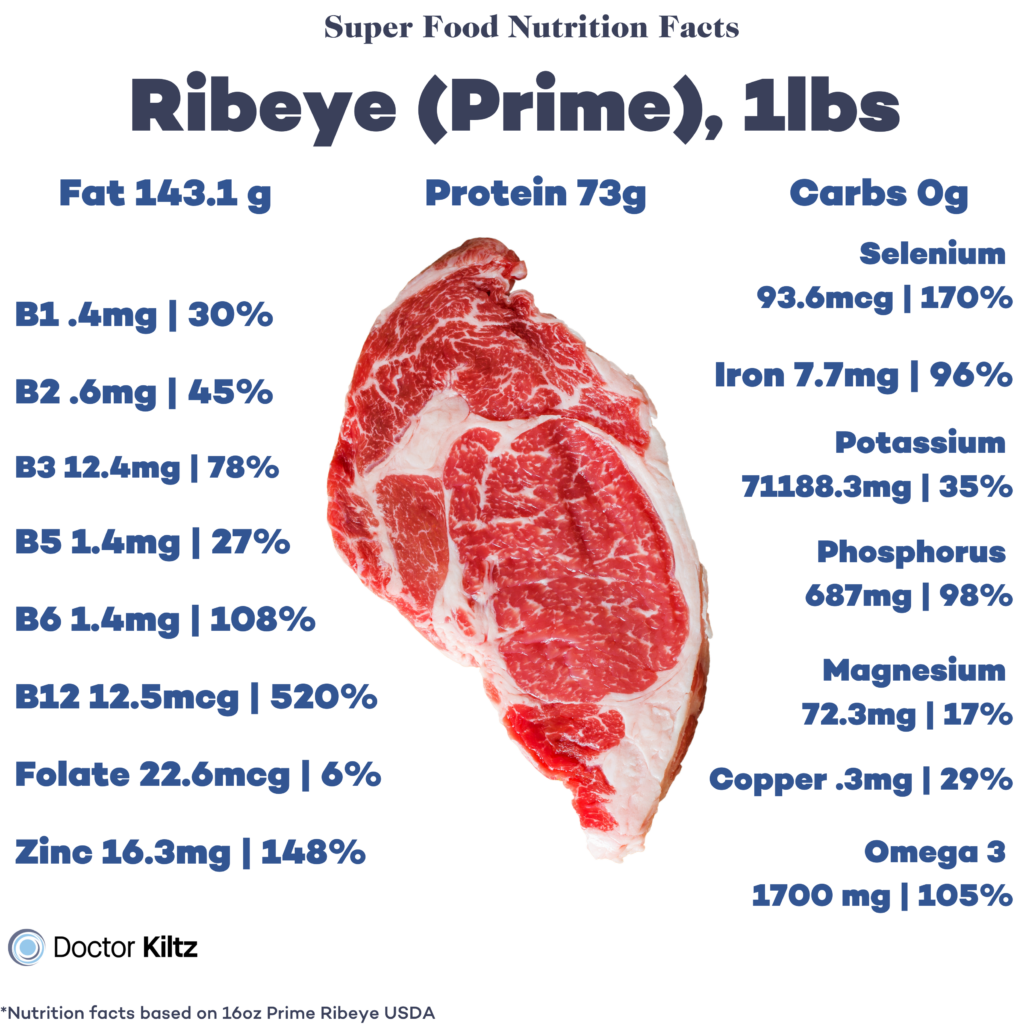
Red meat provides an abundance of micronutrients, many of which are either exclusive to, or only found in abundance in, red meat.
Here’s a rundown of the most potent red-meat-specific nutrients.
Vitamin B12
- B vitamins play an essential role in your body’s ability to convert food into energy
- Promotes the formation of red blood cells that carry oxygen to the brain
- Boosts cognition
- Mood stabilization and powerful anti-depressant effects
- Up to 86% of vegan children, 90% of vegan elderly, and 62% of pregnant vegan women are B12 deficient
- B12 deficiency can result in dementia and is associated with Alzheimer’s disease
Heme Iron
- Only found in meat
- Much more bioavailable than non-heme iron from plant foods
- Essential role in the formation of red blood cells
- Promotes energy metabolism
- Supports proper immune function
- Supports cognition
- Without sufficient iron you will get anemia
Copper
- Essential for converting food into useable energy
- Maintains the integrity of blood vessels
- Plays key role in the formation of connective tissue
- Plays an important role in immune function, nervous system health, gene activation, brain development, hormone metabolism, and fertility
Zinc
- Supports healthy immune response
- In males, low zinc levels are associated with erectile dysfunction and lower sperm count
- Protects against heart disease
- Zinc from animal sources is 400% more bioavailable than zinc found in grains
- Vegans and vegetarians have chronically low zinc levels
- Zinc deficiency inhibits motor and cognitive development in children
- Critical to insulin formation–supports glycemic control for diabetics
Carnosine
- Prevents aging by protecting against damage and shortening of telomeres
- May protect against cognitive decline
- Concentrated in areas of the body with high energy demands, including the heart, brain, and muscles, where it protects from wear and tear
- Prevents glycation–the damaging process of sugar molecules attaching to cells and DNA
- A potent antioxidant
Carnitine
- Boosts male fertility
- Reduces anemia, especially when co-occurring with kidney dysfunction
- Reduces inflammation associated with heart disease
- reducing blood pressure
- Supports brain function
- Supports mitochondrial function and insulin sensitivity for people with type 2 diabetes
- In heart attack patients, carnitine has been shown to prevent ischemia in cardiac muscle
Creatine
- Supports cognitive function
- Improves athletic performance in both vegetarians and omnivores
- Alzheimer’s patients show lower creatine levels
- Supports heart health
- Can improve glycemic control
Taurine
- Strong antioxidant effects
- Reduces glycation
- Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress
- Acts as an antidepressant, likely accounting for the sense of well-being that many people feel after eating meat
CoQ10
- Supports energy generation in cells by making adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- Powerful antioxidant effects linked to anti-cancer properties
- Reduces fatigue
- Increases sperm motility
Benefits of Red Meat: The Bottom line
The many benefits of red meat are attributable to its abundance of both macro and micronutrients.
In fact, red meat provides a complex of essential nutrients in near-perfect proportions for our bodies and in the most bioavailable formats.
The nutrients provided by red meat support numerous physiological functions, including:
- Healthy fertility
- Energy production
- Anti-aging
- Gene expression
- Mental health
- Cognitive ability
- Immune function