We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Is Cheese Healthy? Top 7 Benefits of Cheese

Cheese has held a cherished spot on our plates for centuries. From fresh chevre to robust blues to stalwart cheddar, this dairy delight has been the star of countless dishes. But amidst all this gastronomic pleasure, a question often lingers: Is cheese healthy?
The debate surrounding cheese’s nutritional impact has raged since the 1960s. This was the time when saturated fat was unfairly demonized for an unfounded association with heart disease. Thankfully, modern nutritional science is finally correcting the anti-fat misinformation of years past. Through the lens of modern nutritional science, cheese offers a treasure trove of highly beneficial nutrients, even if some critics still shun cheese for its high fat and calorie content.
Today, we’re here to explore the question, is cheese healthy?
Table of Contents
Is Cheese Healthy? Let’s Talk About Dairy Fat
Any assessment of the health impacts of cheese must begin with the 800-pound gorilla in the room–saturated fat. Dairy fat is mostly saturated.
A meta-analysis (gold standard of research) from 2010 examined 21 relevant studies with data from 347,747 people, and follow-up periods between 5-23 years. Researchers concluded that saturated fats (including dairy fat) was not significantly associated with stroke or heart disease.
Similar findings were published in a 2020 meta-analysis from a global consortium of nutritional scientists in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Researchers concluded, “Whole-fat dairy, unprocessed meat, eggs, and dark chocolate are SFA-rich foods with a complex matrix that are not associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The totality of available evidence does not support further limiting the intake of such foods.”
Looking only at cheese, a 2017 meta-analysis examining nine large-scale studies on the health effects of consuming cheese concluded, “Our findings suggest that long-term cheese consumption was not associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality.”
Now that we’ve set the record straight on dairy fat, let’s take the question, “Is cheese healthy?” to a new depth by looking at the specific benefits of cheese.
1. Cheese Supports Weight Loss
Carrying body fat is not necessarily a health issue. Our bodies are designed to store fat for fuel. However, excess body fat can be a symptom of underlying metabolic issues. Eating cheese can help.
A 2018 study involving over 2,500 men found that after a five-year follow-up, the men who ate higher amounts of cheese had a lower body mass index.
This single study finding was reflected in a review of 16 studies separate studies revealing that consuming more cheese and other high-fat dairy products can lower your risk of obesity.
One of the keys to weight loss benefits of cheese is the satiating combination of high levels of fat and protein, with very few carbs.
This macronutrient offering increases feelings of fullness. When you’re satiated, you’re less likely to snack on high-carb processed foods loaded with vegetable oils and sugars–the substances that are responsible for hormone imbalances and metabolic disorders that drive weight gain.
2. Supports Heart Health

When a food supports weight loss, it’s a safe bet that it also benefits your heart. But when it comes to the research, you don’t even have to bet.
A 2017 analysis of 29 studies with 938,465 combined participants found that people who consumed at least 10 grams of cheese (only ⅓ ounce) per day had a moderately lower risk of cardiovascular disease compared to people who didn’t eat cheese.
A 2023 study looking at the effects of saturated fat from dairy, meat, and plant sources, found that saturated fat from dairy is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Similar findings were reflected in a 2007 study of almost 200 men and women from 45-75 years old. Those who regularly consumed dairy fat had a reduced risk of a heart attack.
One of the keys to the cardioprotective properties of cheese is the presence of fat-soluble vitamin K2. Though not widely known, K2 plays a crucial role in proper calcification (strengthening of bones while preventing the calcification of blood vessels, arteries, and kidneys.
Studies show that for every 10 micrograms of daily K2, the risk of heart disease decreases by 9%.
Many soft cheeses provide between 50 and 100 mcg of K2 per 100-gram serving. Ever popular cheddar provides 24 mcg.
| Cheeses High in Vitamin K2 | Per 100 grams | |
| Jarlsberg cheese | 80 mcg | 66% |
| Munster Cheese | 80 mcg | 66% |
| Soft cheeses (brie, camembert, gouda, creamy blue cheese) | 59 mcg | 49% |
| Edam cheese | 49 mcg | 41% |
| Cheddar | 24 mcg | 20% |
3. Cheese Reduces the Risk of Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder, so it makes sense that the risk of type 2 diabetes is significantly impacted by the foods we eat.
The major European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC), with data from 16,835 healthy and 12,403 diabetic participants from 8 European nations, found an inverse association between eating cheese and fermented dairy with incidences of diabetes.
Consuming just 55 g/d total of cheese and/or yogurt was associated with 12% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes.
4. Reduces Blood Pressure
Even though cheese is often salty, some cheeses can reduce blood pressure.
One study found that consuming 30 grams of Parmesan-like cheese daily was as effective at reducing blood pressure as prescription antihypertensive medication.
These significant effects occur even when consuming the same amount of salt that you’d get a serving of potato chips.
5. Cheese Supports Brain Health
Studies have found that compounds found in Camembert called oleamide and dehydroergosterol reduce inflammation in areas of the brain associated with Alzheimer’s and dementia. Eating cheese rich in these compounds offers protection against neurodegenerative disorders.9
A 2021 study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease found that cheese supports better cognition as you age.
A 2018 study specifically on blue cheese found that it provides neuroprotective properties derived from bioactive compounds that are created when enzymes break down proteins.
6. Anti-Aging Properties

Aged cheese like blue cheese and parmesan, contains numerous bioactive compounds called peptides.
One of these well-studied peptides, called spermidine, has been found to reduce inflammation, increase memory cell formation, and activate autophagy– a process of cellular renewal that removes toxic and degraded organelles from your cells. When not removed, these damaged cell parts can factor in neurodegenerative diseases including dementia, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s.”
Spermidine found in cheese has also been found to slow and reverse aging on the level of cells and organs.
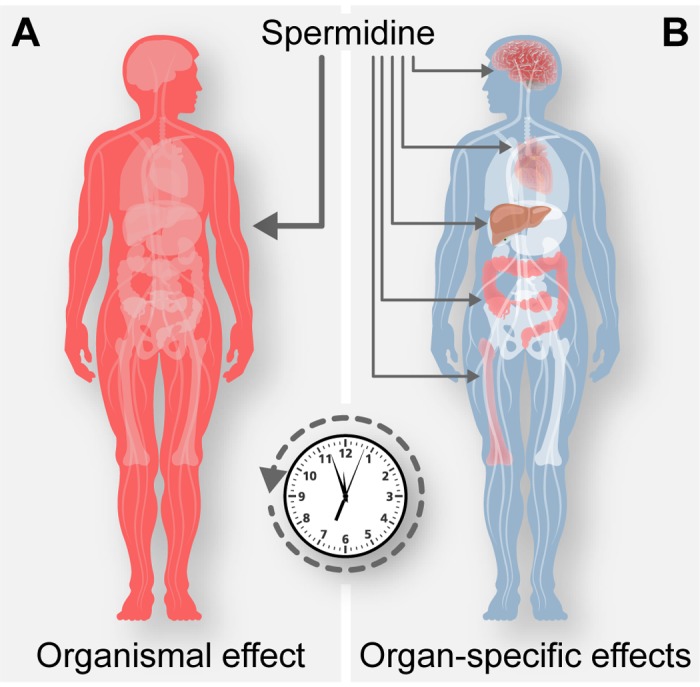
Source: Madeo, Frank & Carmona-Gutierrez, Didac & Kepp, Oliver & Kroemer, Guido. (2018). Spermidine delays aging in humans. Aging. 10. 10.18632/aging.101517.
7. Protection Against Cancer
Cheese from grass-fed dairy is a great source of a beneficial fatty acid called conjugated linoleic acid (CLA).
CLA has been found to significantly inhibit the growth of cancer and tumors in the stomach, prostate, breast, and liver.
A 2005 study found that women who consumed at least four servings of high-fat dairy per day had a 34% lower risk of colon cancer.
A study involving 23 young men found that consuming 5.6 grams of CLA daily decreased inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor and C-reactive protein.
The vitamin K2 we mentioned above has also been found to have anti-cancer properties, slowing the growth of prostate cancer, among other types.
Is Cheese Healthy? Top Benefits of Cheese
Is cheese healthy? Well, when considering the bevy of modern scientific evidence looking at dairy fat, beneficial compounds found in aged cheeses, and generally consuming more or less cheese, the verdict is clear.
Yes, cheese is a remarkably healthy whole food. If you don’t have dairy allergies, there is no reason why you shouldn’t be a cheese connoisseur.
Some of the top benefits of cheese include’:
- Weight loss
- Heart health
- Reduced risk of diabetes
- Reduced blood pressure
- Supports brain health
- Provides anti-aging properties
- Protects against cancer