We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Is Ribeye Healthy? Nutrition, Benefits and More

A thick, juicy ribeye steak is the star on the menus of the most respectable restaurants and the centerpiece of backyard BBQs alike. If you’ve tried Ribeye steak you’ve been seduced by its succulent texture and complex flavor, and you probably want more. But you might be asking, can something this rich and delicious be healthy and nutritious?
The short answer is, yes! Dr. Kiltz makes ribeye the centerpiece of his three pillars of health and wellness. In fact, ribeye is so abundant in macro and micronutrients that you can thrive on a diet of just ribeye steak, salt, and water. This minimalist approach to a carnivore lifestyle is known as the lion diet.
In this article, we’ll explore ribeye nutrition, highlighting the benefits of the many power nutrients that ribeye provides. We’ll also take a look at the modern science supporting the age-old wisdom that fatty meat is remarkably healthy.
Table of Contents
What is Ribeye Steak
The ribeye is cut from the long tender muscle called the longissimus dorsi. It runs from a cow’s hip bone to the shoulder blade.
The tenderness of this cut of steak is due to this being a muscle that doesn’t get much use, which allows for the accumulation of intramuscular fat deposits. When it comes to steak, this fat is described as “marbling.” The more marbled your ribeye is, the juicier and more flavorful it will be.
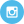
Ribeye Nutrition Facts
Ribeye steak is one of the most nutrient-dense foods on earth. It provides an abundance of bioavailable nutrients, is extremely satiating, and is associated with numerous markers of health, fertility, and longevity [17][18].
Ribeye is loaded with robust amounts of numerous nutrients. Many of these, including B vitamins, zinc, selenium, vitamin D, and iron, are found on the nutritional labels.
But many other vital nutrients in ribeye, like creatine, taurine, and carnosine among others, are not listed by the USDA. Most of these nutrients are found only in meat.
Furthermore, fat, especially the saturated fat found in red meat is often demonized. In reality, saturated fat is an essential nutrient, meaning that we need to get it from our food or we die. There are also various types of saturated fat that have different effects on our health.
When considering the question, “Is ribeye healthy?” the first place to start is ribeye nutrition facts. The USDA “daily value” is the established criteria for nutrient intake of healthy individuals.
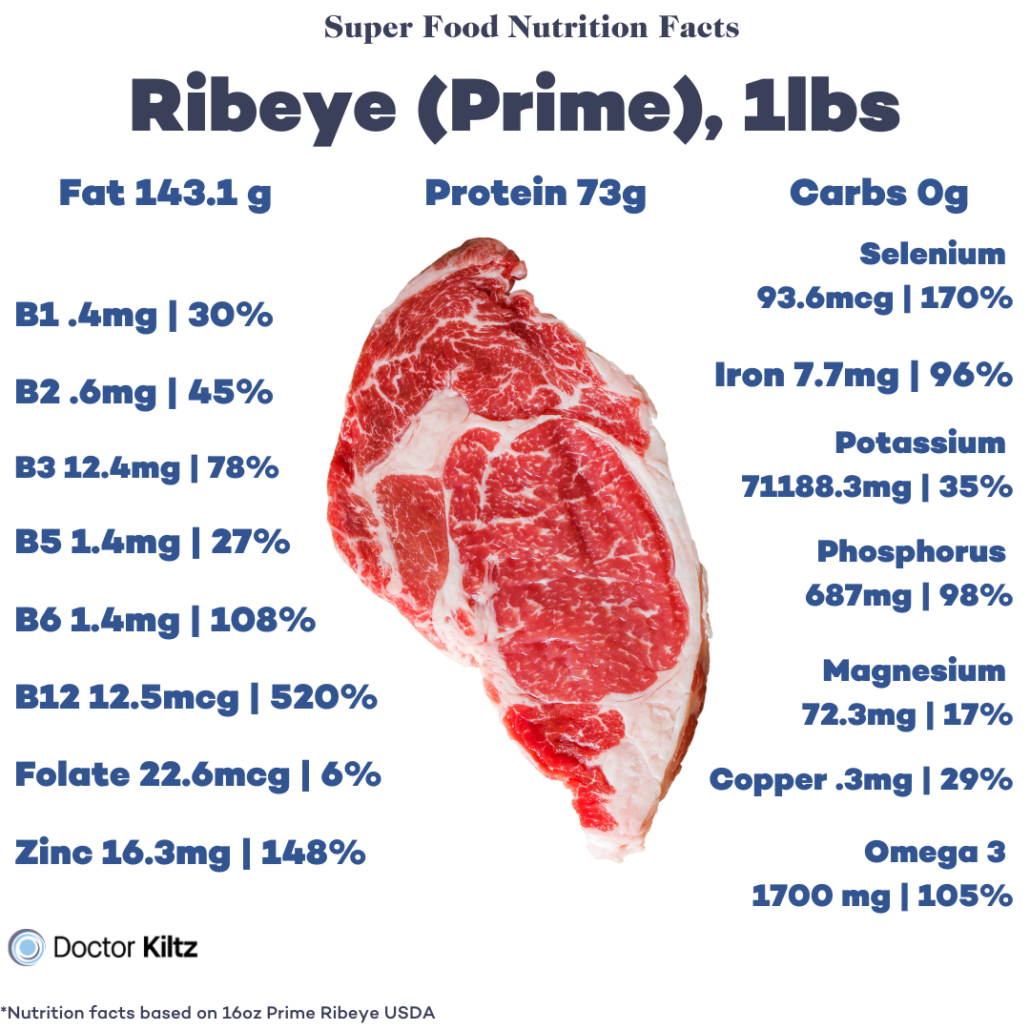
| NUTRIENT | 227G (8 OZ) | |
| Calories | 560 cal | |
| Fat | 34g | |
| Saturated Fat | 12g | |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 12g | |
| Carbs | 0 | |
| Protein | 65g | |
| Vitamins | ||
| B1 (Thiamin) | 25% | |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | 23% | |
| B3 (Niacin) | 119% | |
| B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 30% | |
| B6 | 100% | |
| B9 (Folate) | 7% | |
| B12 | 142% | |
| Vitamin D | 70% | |
| Vitamin E | 7% | |
| Choline | 70% | |
| Minerals | ||
| Magnesium | 12% | |
| Potassium | 14% | |
| Iron | 31% | |
| Copper | 33% | |
| Phosphorus | 42% | |
| Selenium | 131% | |
| Zinc | 111% |
As you can see, ribeye is abundant in both macro and micronutrients. \
Most people think of Ribeye primarily as a protein. And it is true that ribeye provides all seven essential amino acids. Your body needs these proteins to grow and maintain muscle and body tissue [30][31]. But ribeye is more like a natural multivitamin than a protein bar.
Let’s take a look at the many other healthy fats and micronutrients that ribeye provides.
Healthy Fats in Ribeye
Original guidelines for limiting steak had to due with reducing saturated fat intake by cutting out animal fats. These guidelines are derived from unreliable observational studies from the 1950s.
Over the last decade many higher-quality modern studies with over 1 million participants have determined that for the average person, saturated fat is not significantly associated with heart disease, cancer, stroke, diabetes, and death from heart attack [1] [2] [3] [4] [5].
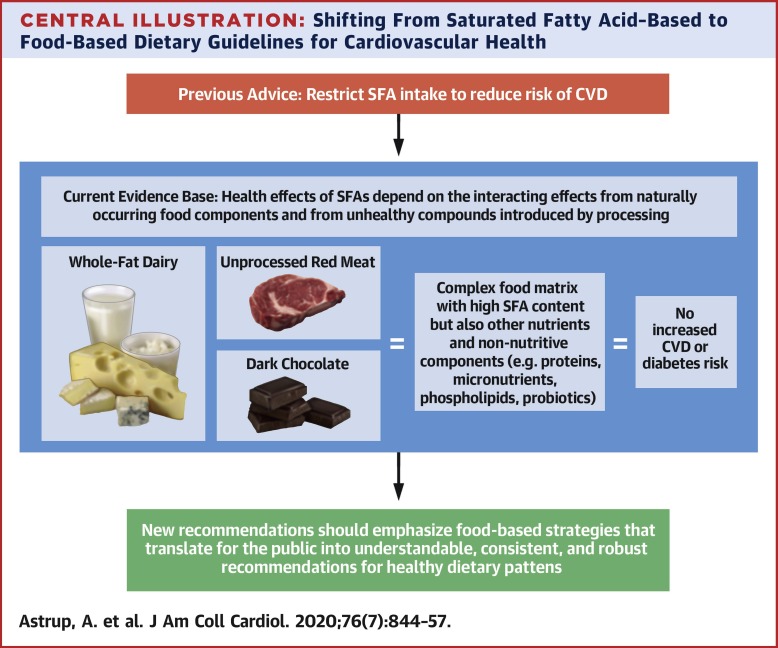
A powerful 2020 study co-authored by researchers from renowned medical schools across the globe and published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found, “Although intake of processed meat has been associated with increased risk of CHD, intake of unprocessed red meat is not, which indicates that the saturated fat content of meat is unlikely to be responsible for this association” [6].
The researcher found that “Whole-fat dairy, unprocessed meat, and dark chocolate are SFA-rich foods with a complex matrix (of nutrients) that are not associated with increased risk of CVD. The totality of available evidence does not support further limiting the intake of such foods” [14].
Such foods in this case include ribeye steak.
In fact, studies show that getting rid of fatty meat like ribeye steak, and replacing it with lean protein like chicken, may increase the risk of certain cancers [17]. This is likely due to the elimination of the fat-soluble vitamin K2 which plays a critical role in removing calcium from arteries and activating the immune-boosting properties of vitamin D.
The high-fat content of ribeye steak also makes it highly satiating. This means you feel fuller faster, and stay full for longer. Making ribeye the centerpiece of your diet can help you eliminate the desire to snack on processed junk foods that feed carb addictions [29].
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) in Grass-Fed Ribeye
Ribeye steak, especially when pasture-raised and grass-fed, offers significant amounts of a highly beneficial fat called conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) [32].
Grass-fed meat and dairy contain 300-500% more CLAs than grain-fed varieties.
CLA may have powerful anti-cancer properties. In a Finnish study, women with adequate CLA levels had a 60% lower incidence of breast cancer [3]
Tests on mice comparing a diet of high CLA beef, to a diet of low CLA beef found that consuming more CLA “exerts profound antiinflammatory effects” [4].
Monounsaturated Fat
⅓ of the fat in ribeye steak is monounsaturated fat.
Studies show that monounsaturated fat is anti-inflammatory and may reduce the risk of heart disease [26][27].
Stearic Acid in Ribeye
Stearic acid is one of the most abundant fatty acids in ribeye, accounting for ⅓ of the saturated fat content.
Stearic acid has been shown to improve body fat ratio, support mitochondrial function–the energy factories inside your cells– and promote weight loss [38] .
Considering its effects on LDL (bad) cholesterol, stearic acid has been shown to lower or have a neutral effect [39].
Micronutrients in Ribeye Steak and Their Benefits
The micronutrients in ribeye steak contribute to and support numerous health benefits, including:
- Supports fertility in men and women
- Energy production
- Weight loss
- Anti-aging
- Antioxidant effects
- Gene expression
- Better mood
- Cognitive and neurological health
- Stimulated stem cell production
- Supports immune function
Let’s take a look at some key nutrients in ribeye steak and how they can support your health.
Ribeye for Cognitive Performance
If you’re looking for more cognitive power and sustained focus, adding ribeye steak may offer a boost.
A matric of powerful nutrients found in abundance in ribeye steak work synergistically to support and enhance cognitive function. These include:
- Selenium
- Copper
- Niacin (Vitamin B3) [30]
- Iron
Selenium
At 131% of your RDV selenium per 8 oz serving, ribeye is an abundant source of this thyroid-supporting and immune-boosting nutrient.
Selenium plays a key role in the endogenous production of special proteins called selenoproteins. These proteins are critical to reproductive health and DNA synthesis [19].
Selenium also provides antioxidant properties–which is why you don’t need to eat fruit to get antioxidants.
As an antioxidant, selenium reduces oxidative stress by eliminating free radicals [20]. It also has the knock-on effect of increasing levels of another powerful antioxidant, glutathione [21].
The selenium in ribeye may have powerful anti-cancer properties. A review of 69 studies with data from 350,000 participants showed that high blood levels of selenium were associated with a lower risk of various cancer types, including lung, breast, colon, and prostate cancers [22].
Other studies highlight the possible neuroprotective benefits of selenium, revealing that patients with Alzheimer’s disease have low levels of selenium [23][24].
Selenium also supports healthy lung function. A study on patients with asthma found that those with higher levels of selenium had better lung function [25].
B Vitamins
Ribeye is a fantastic source of numerous B vitamins, including over 100% of B3, B6, and B12.
B vitamins play a key role in the process of converting food into usable energy. They promote the formation of red blood cells that carry oxygen to the brain, boost cognition, stabilize mood,t [41]
B12 is found almost exclusively in meat. Up to 86% of vegan children, 90% of vegan elderly, and 62% of pregnant vegan women are B12 deficient [42].
B12 deficiency can result in dementia and is associated with Alzheimer’s disease [43]
B12 can act as a powerful antidepressant, which may partly explain the experience of euphoria that many people describe after eating ribeye steak [44].
Heme Iron
A serving of ribeye provides 31% of your RDV in iron. Yet the heme iron only found in red meat like ribeye is significantly more bioavailable (useable) than iron from plant foods like grains [1].
Iron plays an essential role in the formation of red blood cells, promotes energy metabolism, supports a healthy immune system, and is critical to cognitive ability [46] [47] [48] [49].
Copper
A serving of ribeye provides 33% of your RDV in copper. This mineral plays a critical role in creating energy and maintaining the integrity of blood vessels. It’s also an important component in the formation of connective tissue, immune function, nervous system health, gene activation, brain development, hormone metabolism, and fertility [50].
Yet most people don’t consider their copper intake. One way to remain blissfully ignorant is to simply eat ribeye steak.
Zinc
Ribeye is a fantastic dietary source of ribeye, providing 111% per 8 oz serving.
Low levels of zinc are associated with erectile dysfunction and lower sperm count in males [51]
As with other minerals, the zinc in steak is 400% more bioavailable than zinc from grains like breakfast cereals [52].
Not surprisingly, studies show that vegans and vegetarians are low in zinc [53]. Plant foods, especially grains, contain to phytic acid that blocks zinc absorption.
Zinc deficiency affects motor development and cognitive development in children [54]
Getting sufficient and bioavailable zinc from ribeye steak can help support heart health, the formation of insulin, and increase glycemic control [55].
Carnosine
Carnosine is a promising anti-aging compound found exclusively in red meat like ribeye steak [1]
Interestingly, carnosine is concentrated in areas of the body with high energy demands, including the heart, brain, and muscles, and plays a role in protecting these parts from wear and tear. Part of its protective power has to do with how it prevents glycation–the damaging process of glucose molecules attaching to cells and DNA.
Though the USDA does not test specifically for carnosine, research suggests that ribeye contains around 400 mg per 100 grams.
Studies looking at carnosine have found that it offers numerous powerful benefits including:
- Inhibits glycation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) by reactive aldehydes (6).
- Helps minimize early-stage lipoxidation (7).
- In an experiment, human cell cultures were treated with high concentrations of carnosine as in Petri dishes. When these cultures were moved to other Petri dishes without carnosine, their appearance changed to resemble the same age as the control group of untreated cells (8) (9).
- In a study involving rats, researchers found that the carnosine released from muscles during exercise regulated the autonomic nervous system with the result of improving blood glucose levels (10).
- Act as a chelating (binding) agent for harmful metal ions coming from copper, iron, and zinc. Carnosine can bind to harmful ions coming from minerals copper, iron, and zinc. Ions from these minerals are found in higher concentrations in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease (11). In this way, the carnosine found in ribeye can support the safety of the minerals found in ribeye.
- Carnosine may offer anti-inflammatory effects in an area of the brain called the striatum, which may offer protection against neurodegeneration (12).
- Carnosine can help protect against the inactivation of esterase which has been associated with cataracts and Alzheimer’s disease. (13).
- Carnosine inhibits the mTOR and TGFß/Smad3 pathways. This inhibiting property reduces the side effects of reactive carbonyl compounds associated with aging(14).
- In a study involving mice, carnosine supplementation reduced the effects of acute spinal cord injury (poor mice!) (15)
One point to consider with carnosine is that it has a very short half-life in the body, so to stay replete you have to eat carnosine-rich foods often.
Carnitine
Carnitine is another compound found almost exclusively in ribeye and other meats.
Studies show that creatine plays a vital role in improving and supporting male fertility increasing sperm motility and morphology [5].
When co-occurring with kidney dysfunction carnitine reduces anemia [6].
Studies on people with type 2 diabetes show that carnitine may play a major role in mitochondrial function and insulin sensitivity [7].
In heart attack patients, carnitine has been shown to prevent ischemia in cardiac muscle [8].
Creatine
Steak offers around 5g of creatine per kg. The recommended supplementation of creatine is 5grams, so if you’re eating lots of steak on a keto die or following a carnivore diet meal plan, you may be meeting your creatine goals without even knowing it.
Creatine has been popular among weightlifters for decades, but it provides many other benefits that most people are unaware of.
Studies on creatine provide numerous insights into its possible benefits including:
- Improves athletic performance improves in both vegetarians and omnivores [5]
- When vegetarians add creatine supplements to their diets they show improved cognitive function [6]
- Alzheimer’s patients show lower creatine levels [7]
- Improves cardiovascular performance in patients with heart failure [9]
- For people with type 2 diabetes, supplementing with 5g of creatine per day combined with exercise improves glycemic control [9]
Taurine
Just 3-oz of ribeye steak provides 55 mg of taurine, around 70% of the daily taurine requirement by healthy adults.
Taurine is considered a provisionally essential amino acid, meaning your body needs you to get it from food in times of stress. Otherwise, it can make enough to survive by synthesizing it from other proteins.
However, unlike other amino acids, taurine isn’t the building block of proteins. It plays a key role in numerous critical bodily functions including [2][3][4]:
- maintaining electrolyte balance in your cells
- Maintaining hydration
- Forming bile salts that play a key role in digestion–this is especially important when you’re practicing a low-carb high-fat diet
- Regulates minerals in your cells
- Supports central nervous system function
- Supports eye function
- Regulates immune system health and antioxidant function
- Reduces glycation
- Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress
- Antidepressant effects. Along with B12 taurine contributes to the feelings of well-being that many people report after eating steak [9]
What Science Says about Ribeye and Your Health
As mentioned above, there have been many recent studies over the years correcting the record on the health benefits and risks of steak.
Meat Does Not Cause Cancer
A 2011 analysis of 25 studies found insufficient evidence to support an association between steak and colon cancer–the most common cancer attributed to eating steak [16].
Eating Meat Promotes Longevity
Studies show that total meat consumption correlates with greater life expectancy. And these findings are independent of total caloric intake, economic status, urban advantages, and obesity [16].
High-Steak Low-Carb vs. Vegetarian Diets
The association of meat with longevity is likely a result of specific health benefits promoted by meat.
Studies comparing low-carb, high-fat diets high in the steak to vegetarian diets have revealed dramatically better outcomes for the high-steak diets. The superior health markers of meat-eaters include cardiovascular health, weight loss, and blood sugar regulation [19][20][21].
We Evolved Consuming a Diet of Fatty Meat
We, modern humans, share nearly identical physiology with our caveman ancestors.
Recent studies out of Tel Aviv University provide strong evidence that for nearly 2 million years of human evolution our ancestors evolved and adapted to thrive on a diet consisting of mostly fatty red meat like ribeye steak–but cut from megafauna like mastodons and wooly mammoths [22].
When considering that our bodies evolved on meat, it makes sense that ribeye steak provides an almost perfect balance of highly bioavailable macro and micronutrients.
Eating Regeneratively Raised Steak Can Benefit the Environment
Meat can be farmed with “regenerative agricultural practices” or “carbon farming.” Doing so can sequester carbon and improve soil health [23].
At current rates, industrial agriculture of plant foods will destroy all arable topsoil in 60 years [24]
One way to scientifically approach the question of steak being healthy is by looking at studies that compared diets high in steak to vegetarian diets.
Eating Ribeye Steak And Reducing Plant Foods Can Protect you From Toxins and Antinutrients
Ruminant animals like cows can eat, digest, and ferment plant foods into fatty acids that become part of their meat.
We humans can’t digest most parts of plants. So we end up absorbing their carbs while exposing ourselves to various plant defense mechanisms, including thousands of different plant toxins and antinutrients.
Opting for ribeye over plant foods reduces your exposure to added sugars, processed grains, and industrial vegetable oils. This is also why steak on keto or as the centerpiece of essentially any diet is a healthy choice.
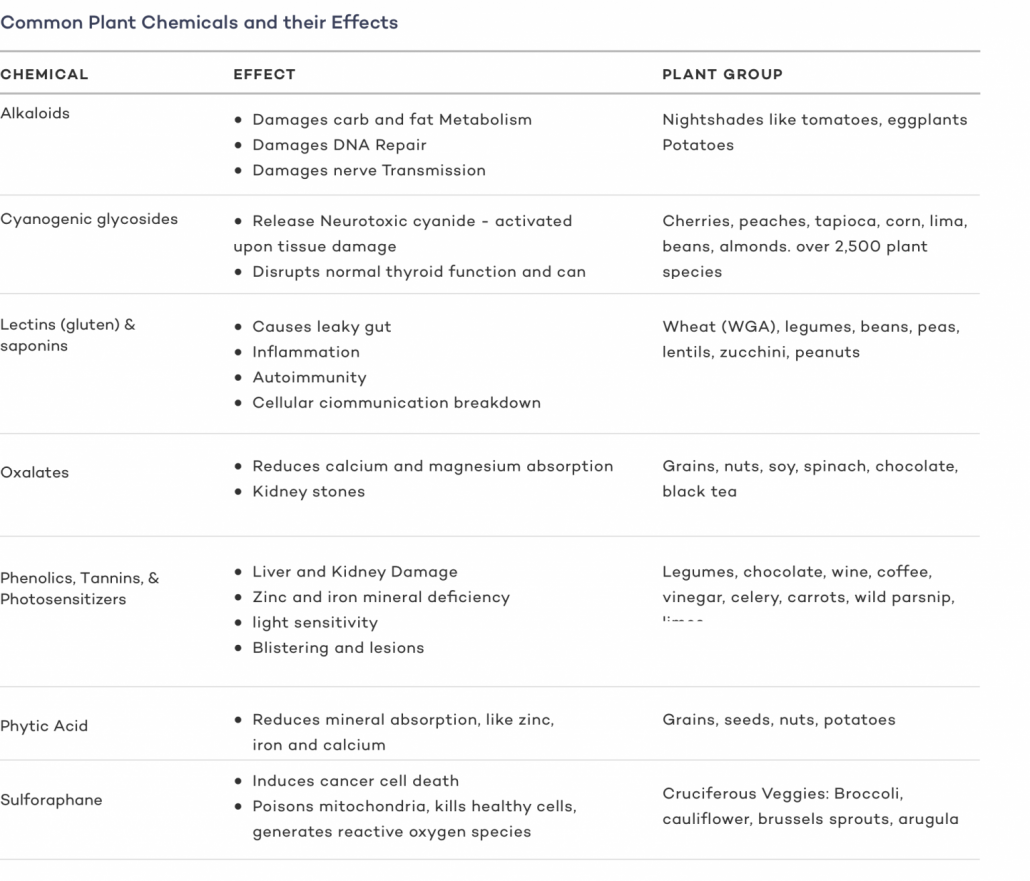
In the chart below you can take a look at some common plant toxins and their effects:
All of these compounds can contribute to chronic inflammation, heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and numerous other negative health outcomes [26] [27] [28] [29].
Is Ribeye Healthy: The Takeaway
When considering only the maco and micronutrients measured in ribeye steak, it is clear that ribeye is unequivocally healthy.
In support of the healthiness of ribeye steak, we can look at numerous modern studies confirming that consuming saturated fats when part of a whole foods matrix of nutrients (like ribeye) is not linked to cancer, stroke, or cardiovascular disease.
The totality of evidence suggests that ribeye is indeed an extremely healthy food.
If you are practicing a carnivore elimination diet by eating only ribeye, salt, and water, it is important to note that ribeye does not provide Biotin (B7), or chromium–both important nutrients. This diet can be effective in the short term, but in the long term, you will likely want to add in eggs, liver, and dairy for healthy doses of these missing nutrients.