We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Carbs in Cheese? List of High and Low-Carb Cheeses

Cheese has been a beloved food worldwide since its invention nearly 10,000 years ago. However, if you’re among the millions of people turning to a low-carb diet like paleo, keto, or carnivore, you may wonder about the carbs in cheese. Or even asking the question, “Does cheese have carbs?”
The short answer: While some types of cheese have low-to-no carbs, others can be surprisingly high.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the carbs in cheese, explore the different types of cheese and their carb contents, and discuss the potential health implications of consuming cheese as part of a low-carb diet.
Table of Contents
Health Benefits of Eating Low-Carb Cheese

Before jumping into our list of high and low-carb cheeses, let’s explore just why cheese deserves your consideration.
Cheese is so common that most of us aren’t aware that it’s actually a healthy, nutrient-dense whole food with numerous clinically studied health benefits.
The notion of cheese as a healthy food might be especially strange for those of you who have been indoctrinated by bogus low-fat diet fads. So, let’s take a minute to debunk the “fat is bad” dogma.
Dairy Fat is Healthy
If you’re already enjoying the benefits of a low-carb diet rich in fatty whole foods, the idea that dairy fat is healthy and nourishing is old news. But for the rest of you, here are a couple of major studies to consider.
- In 2010 a major meta-analysis (gold standard of research) was published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Researchers examined 21 previous studies involving 347,747 people, with a follow-up period of between 5-23 years. The study concluded that consuming saturated fats (including dairy fat) was not significantly associated with stroke or heart disease.
- In 2020, a bellwether paper published in the leading Journal of the American College of Cardiology, concluded, “Whole-fat dairy, unprocessed meat, eggs, and dark chocolate are SFA-rich foods with a complex matrix that are not associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The totality of available evidence does not support further limiting the intake of such foods.”
- In a 2017 meta-analysis examining 9 large-scale studies on the health effects of consuming cheese concluded, “Our findings suggest that long-term cheese consumption was not associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality.”
- A 2013 meta-analysis looking at the effects of low-carb, high-fat diets found that they are clinically effective for combating numerous disorders, including metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, acne, PCOS, and neurological issues, including epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease.
Benefits of Consuming Cheese
Not only is cheese not harmful, it has been shown to offer numerous health benefits. Let’s take a look at some of the most studied benefits.
Reduces Risk of Diabetes
The massive 2009 European Nutrition (EPIC) study examined data from 16,835 healthy and 12,403 diabetic participants across 8 European nations.
Researchers identified an inverse association between eating cheese and fermented dairy with incidences of diabetes. In simple terms, more cheese, less diabetes.
Interestingly, the data got remarkably detailed: Consuming only 55 grams of total cheese and/or yogurt was associated with a 12% reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
Reduces Blood Pressure
Even cheese with relatively high carb concentrations, like Grana Padano (essentially a parmesan cheese), has been found to reduce blood pressure.
A 2018 study found that eating 30 daily grams of Grana Padano was as effective at lowering blood pressure as prescription antihypertensive medications.
What’s more, this is an extremely salty cheese–equal to consuming a serving of potato chips. Salt can increase blood pressure, but the effects of the cheese offset the sodium.
Weight Loss
A large 2018 study with data from over 2,500 men found that after five years, participants who consumed higher amounts of cheese had a lower body mass index.
Similar findings were revealed in a meta-analysis of 16 studies that showed cheese and other high-fat dairy products appear to lower the risk of obesity.
If you’re wondering how a high-calorie food like cheese aids in weight loss, just think of how filling cheese is.
When you’re satiated from eating cheese, you’re less likely to snack on junk made with toxic seed “vegetable oil” or binge on sugar-loaded processed foods.
Neurological Protection
Aged cheeses like blue cheese and camembert contain special compounds that can reduce inflammation, thereby protecting your brain.
A 2018 study discovered that oleamide and dehydroergosterol found in Camembert reduced inflammation in areas of the brain associated with Alzheimer’s and dementia, leading researchers to deem cheese containing these compounds as a neuroprotective food.
Not surprisingly, a 2021 study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease found that consuming cheese is associated with improved cognition as we age.
Supports Heart Health
Studies show that regularly consumed dairy fat (like you find in cheese that is both high and low in carbs) is associated with a reduced risk for heart attacks.
One of the keys to the cardioprotective benefits of cheese is likely the presence of vitamin K2.
For every ten micrograms of K2 you consume daily, your risk of heart disease decreases by 9%.
This is an area where the carbs in cheese don’t really matter. However, soft cheeses generally contain more K2, as you’ll see in the list below.
| Carnivore Diet Cheeses High in Vitamin K2 | Per 100 grams | |
| Jarlsberg cheese | 80 mcg | 66% |
| Munster Cheese | 80 mcg | 66% |
| Soft cheeses (brie, camembert, gouda, creamy blue cheese) | 59 mcg | 49% |
| Edam cheese | 49 mcg | 41% |
| Cheddar | 24 mcg | 20% |
Anticarcinogenic
Cheese made from grass-fed dairy can be a great source of a beneficial fatty acid called conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
Studies have found that CLA can significantly inhibit cancer and tumors in the stomach, prostate, breast, and liver.
The presence of CLA in cheese is likely a factor in the results of a 2005 study that found that women who ate four servings of high-fat dairy per day benefit from a 34% reduction in the risk of colon cancer.
Another study on young men found that consuming 5.6 grams of CLA per day reduced inflammatory markers associated with cancer.
The vitamin K2 in cheese may be another key factor in its anticarcinogenic properties, with new studies suggesting that K2 can impede the spread of various cancers, including prostate cancer.
Carbs in Cheese? Top 4 Low-Carb Options
These 4 delicious low-carb cheeses provide more than healthy fats and proteins.
Modern research is catching up with what traditional cheese-making cultures have known for millennia–that cheese provides a special blend of powerful nutrients produced in the culturing process that you cannot get in any other food.
1. Blue Cheese
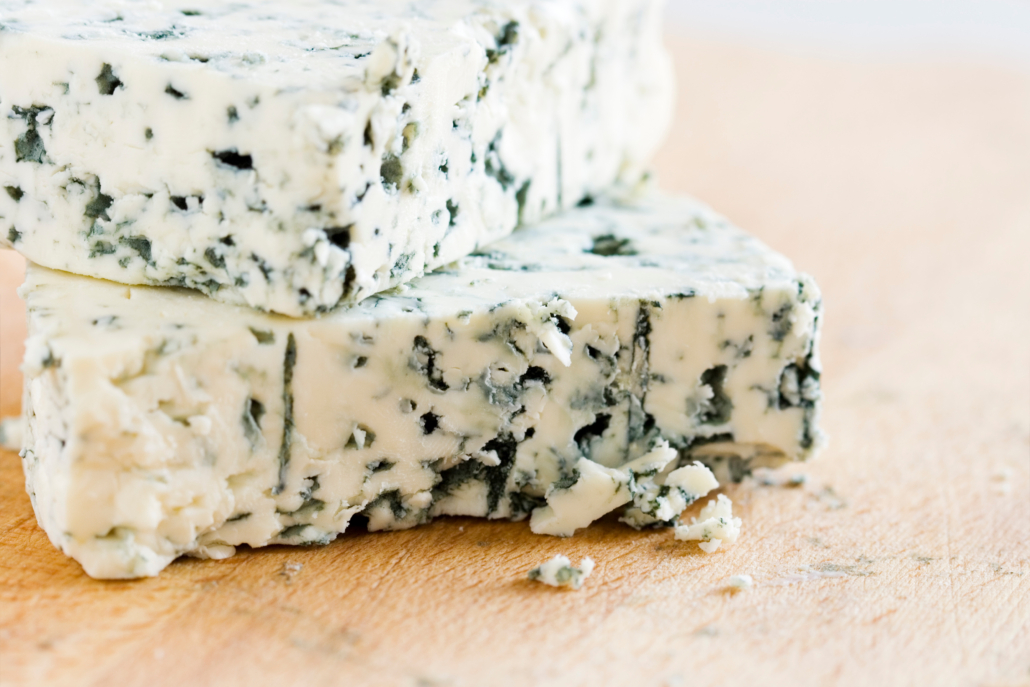

The carbs in blue cheese are negligible, with only .2g per 100-gram serving.
So if you’re eating only a couple of tablespoons (30 grams) at a time, you can consider blue cheese zero-carb food.
Like other specially cultured cheeses, blue cheese contains between 2900 and 4700 different beneficial bioactive peptides that get created as enzymes break down dairy proteins.
These bioactive compounds are likely factors in the numerous studied benefits of blue cheese, including
- lower cholesterol levels
- Prevention of inflammation in arteries
- reduced blood clotting in veins
- reduce joint pain and arthritis relief
One compound called spermidine, found in high concentrations in blue cheese (262 nmol/g) has been found to provide both cardioprotective and anti-aging properties.
| Nutrients per 100g of Creamy Blue Cheese | |
| Calories | 425 |
| Fat | 43.3g |
| Saturated Fat | 26.7g |
| Carbohydrates | .2g |
| Protein | 13.3g |
| Fat: protein | 3.25:1 |
| Significant Vitamins and Minerals | |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) | 1.7mg 35% RDA |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.4mg (36% RDA) |
| Selenium | 8.6µg (16%) |
2. Muenster
How many carbs are in muenster cheese? Only 1.1 grams per 100 grams.
The highest quality and most nutritious Muenster is made from unpasteurized “raw” cow’s milk in the summer in autumn. This is how it’s been done since it was invented by monks in northeastern France in the Middle Ages.
Yes, Muenster cheese can be particularly stinky, but that’s a sign of the kind of enzymatic breakdown that produces beneficial bioactive peptides.
Munster is also the top dog when it comes to boosting your vitamin K2 intake: 801 ng/g.
Wisconsin Cheese Company makes a great muenster.
| Nutrients per 100g of Muenster | |
| Calories | 332.5 |
| Fat | 29.8g |
| Saturated Fat | 18.9g |
| Carbohydrates | 1.1g |
| Protein | 23.1g |
| Fat: protein | 1.3:1 |
| Significant Vitamins and Minerals | |
| Vitamin A | 25% RDA |
3. Goat Cheese
Carbs in goat cheese? This one’s easy. Zero, zilch, nada.
Goat cheese has been consumed in the Mediterranean region for thousands of years. And it remains a popular ingredient in dishes from Greece, Italy, and other neighboring countries.
Historians believe that goat cheese may have been one of the earliest types of cheese produced, as goats were among the first domesticated animals.
Recent studies have shown that goat cheese may improve heart health, boost the immune system, and aid in weight loss.
Additionally, goat cheese is typically lower in lactose than cow’s milk and doesn’t contain casein. This makes it a great alternative for people with lactose intolerance or milk protein allergy.
| Nutrients per 100g of Goat Cheese | |
| Calories | 332.5 |
| Fat | 21 g |
| Saturated Fat | 15 g |
| Carbohydrates | 0 g |
| Protein | 19 g |
| Significant Vitamins and Minerals | |
| Vitamin A | (1,464 IU)150% RDA |
4. Goat’s Milk Gouda
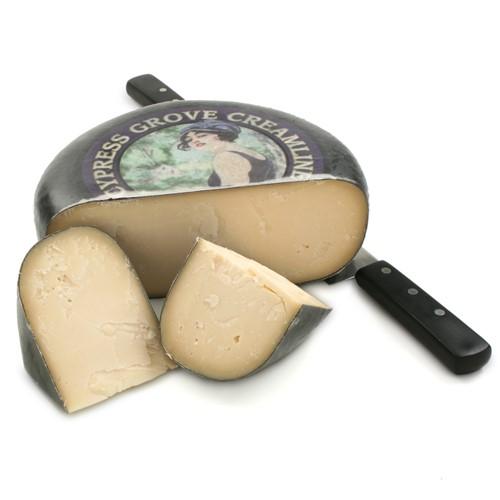

Does Gouda cheese have carbs? Not when it’s made from goat’s milk!
This common, traditional cheese from Holland becomes a specialty superfood when made from goat’s milk. This makes it a great option for people seeking A2 alternatives to cow’s milk.
And studies have shown that goat’s milk is also high in medium-chain fatty acids, which are easily absorbed and metabolized by the body for energy, making goat’s milk Gouda an excellent choice for athletes or anyone looking to boost their energy levels.
Midnight Moon from Cypress Grove is a gouda that has been aged six months, creating a nutty, buttery flavor and a “sweet” caramel finish.
“Midnight Moon” is one of the tastiest low-carb cheeses we’ve ever tried. It’s nutty, caramelly, and goes extremely well with zero-carb snacks like cured meats.
| Nutrients per 100g of goat milk Gouda | |
| Calories | 378 |
| Fat | 42g |
| Saturated Fat | 24.5g |
| Carbohydrates | 0g |
| Protein | 28g |
| Fat: protein | 1.5:1 |
| Significant Vitamins and Minerals | |
| Vitamin A | 25% RDA |
Carbs in Cheese? 4 High-Carb Cheeses
These four common kinds of cheese have more carbs than most types of cheese. Though canned and processed cheese should be eliminated. The other natural cheeses are healthy despite their carb content and can still be consumed in moderation on a low-carb diet.
1. Canned Cheese
Carbs in canned cheese? You betcha—1 gram per tablespoon, or 7 per 100 grams.
But beyond the carbs in canned cheese, there are other reasons why it should be eliminated from both high and low-carb diets.
For one, canned cheeses are highly processed industrial products. In fact, by law, they only have to be 51% actual cheese.
What’s the rest of it, then? Stuff like reconstituted dairy proteins, artificial emulsifiers, and toxic seed oils.
The macros are not super keto-unfriendly: 6g of protein, 2 grams of carbs, 5 grams of protein per serving. But you can get these from much healthier whole foods.
2. American Cheese
Carbs in American cheese: 9 grams per 100-gram serving.
Like canned cheese, American cheese is a highly processed industrial product. It often contains additives and preservatives.
The low-quality dairy products used to make American cheese is sourced from factory farms where animals are subjected to poor living conditions and fed with hormones and antibiotics.
Compared to traditional, unprocessed cheeses, American cheese is low in essential nutrients such as protein, calcium, and vitamins.
| Nutrients per 100g of Kraft Singles American Cheese | |
| Calories | 330 |
| Fat | 24.5 g |
| Saturated Fat | 14 g |
| Carbohydrates | 9g |
| Protein | 18 g |
3. Cottage Cheese
Unlike the processed cheeses above, cottage cheese isn’t off-limits due to nutritional and quality issues.
However, on a zero-carb or low-carb diet, you’ll need to beware of how quickly the carbs in cottage cheese can add up. Especially if you’re like most people who find it so yummy that they can’t help but devour an entire carton in a sitting.
1 cup of full-fat cottage cheese contains 6.8 grams, along with a mega-dose of 24.6 grams of protein. Remember that low-carb eating calls for high-fat and moderate protein. If you eat too much protein, your body just turns it into glucose.
It is possible to find higher fat cottage cheese (8%). But if you want to enjoy cottage cheese on low-carb diets go ahead and boost the fat yourself by adding heavy cream or creme fraiche. If you have it with more savory faire, add olive oil, sour cream, and chopped olives.
| Type of cottage cheese | Calories | Carbs | Fat | Protein |
| 8% Milk Fat Keto Cottage Cheese | 300 | 6 grams | 18 grams | 28 grams |
| 4% Full fat | 281.2 | 6.8 grams | 9 grams | 25.6 grams |
| 2% Reduced fat | 162 | 10 grams | 4 grams | 20 grams |
| 1% Reduced fat | 144 | 6 grams | 2 gram | 24 grams |
| Nonfat | 144 | 14 grams | 0 grams | 20 grams |
| Low fat with pineapple and cherry | 195 | 26 grams | 2 gram | 18 grams |
| Low fat with garden vegetable | 196 | 8 grams | 8 grams | 22 grams |
4. Parmesan
How many carbs are in Parmesan cheese? More than most people think.
100 grams of parmesan contributes 14 grams of carbs.
Yet, it’s so savory and flavorful that most people only use small-ish amounts. Considering that is only contributes 0.9 grams of carbs per tablespoon, parmesan cheese is actually a decent low-carb option.
And as we mentioned above, it may provide cardioprotective peptides.
Carbs in Cheese: The Bottom Line
Does cheese have carbs? Some do, some don’t. But even unprocessed higher-carb cheeses like parmesan and cottage cheese can be enjoyed in moderation on a low-carb diet.
That said, the lowest carb cheese on our list are also the types that contain the highest levels of beneficial bioactive peptides and vitamin K2.
Some great low-carb cheese options include blue cheese, Muenster, goat cheese, and goat gouda.
By incorporating these cheeses into your low-carb meals and snacks, you can enjoy delicious and satisfying dishes while still staying within your carb goals.