We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Top 15 CoQ10 Foods and Benefits

CoQ10 is the shorthand for Coenzyme Q10, a fat-soluble compound that creates energy in your cells and provides powerful antioxidant protection against damage and disease from free radicals. Your body makes CoQ10 on its own, but as you age, your CoQ10 levels drop, and it may be important to boost your levels with CoQ10 foods.
Your body makes and stores CoQ10 in the energy factories within your cells called mitochondria. It is found in especially high concentrations in important organs, including the heart, liver, and lungs.
Why does CoQ10 matter? Studies show that diseases and disorders, including cognitive decline, diabetes, heart disease, and various cancers are linked to low CoQ10.
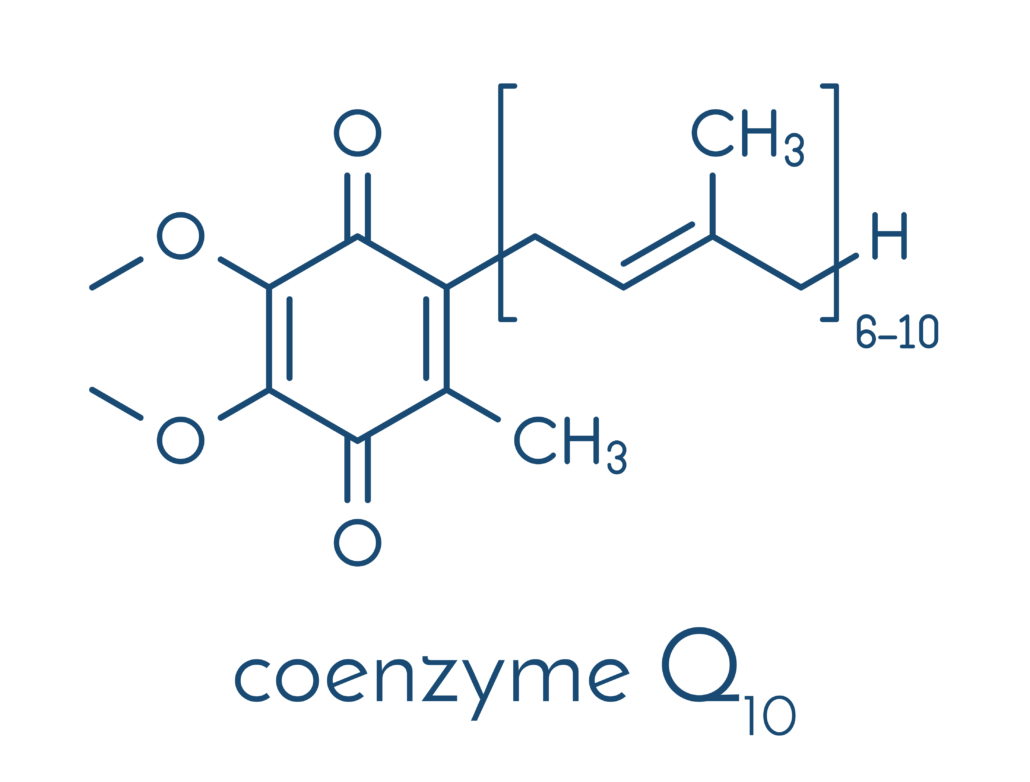
Table of Contents
Factors in CoQ10 Deficiency
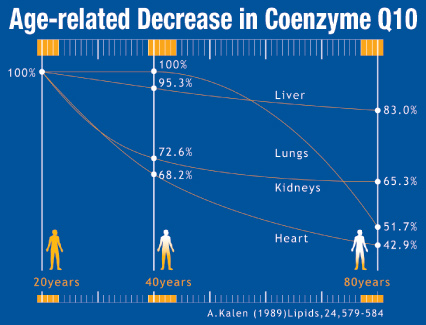
CoQ10 levels in the body begin dropping as early as your 20s, and your body’s ability to produce CoQ10 also declines with age.
Yet there are other factors in CoQ10 deficiency, including,
- Vitamin B6 deficiency
- Mitochondrial diseases
- Genetic abnormalities that inhibit CoQ10 production
- Oxidative stress caused by high-carb eating
- Damage from statins
If you have any of the above disorders a diet high in CoQ10 foods can help keep your body replete.
What is CoQ10 Good For?
Thanks to its powerful antioxidant and cellular energizing properties, CoQ10 is good for a number of vital physiological functions, including heart health, cognition, skin health, reproductive health, and protection against cancer.
Before jumping into the list of CoQ10 foods, let’s look at some of the studied benefits of CoQ10.
Supports Heart Health
Studies show that CoQ10 can reduce heart disease risk factors, reduce hospitalizations of heart disease, and reduce the risk of dying after heart failure. 11 12
Researchers theorize that CoQ10 supports and helps the heart heal by reducing oxidative damage and revitalizing cellular energy production.
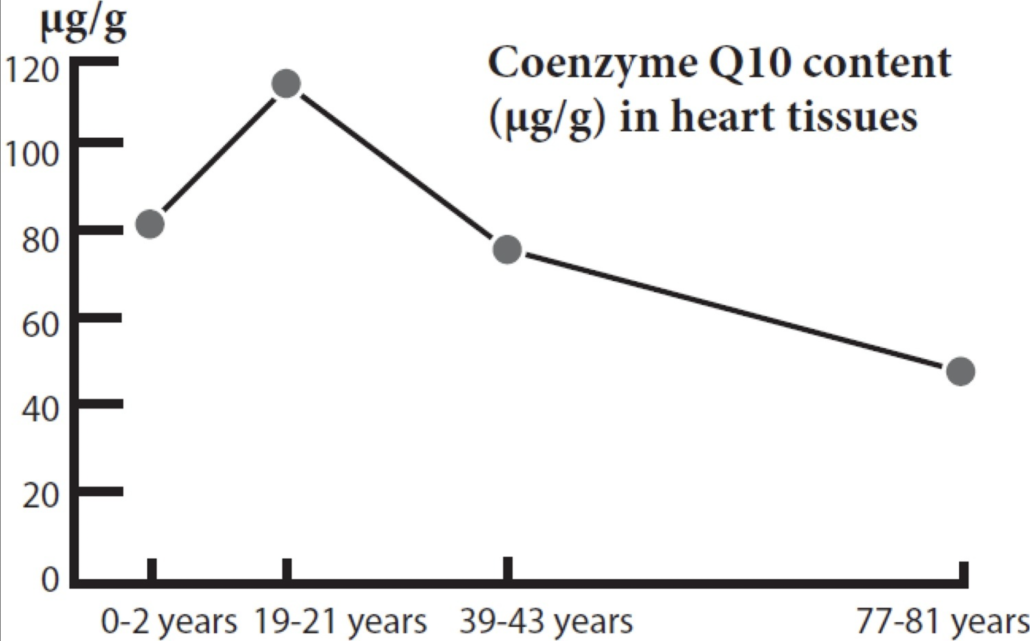
Fig. 3. Effects of aging on CoQ10 concentrations as measured in heart tissue cells (Kalén et al., 1989).
Supports Brain Health
Because the brain is high in fatty acids and requires abundant oxygen, it is especially susceptible to oxidative damage.
Oxidative damage in the brain can lead to the production of harmful compounds that interfere with memory and cognition.48 49
Age-related mitochondrial decline can also result in brain cell death associated with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. 47
CoQ10 may protect against oxidative stress in the brain while improving mitochondrial function. 50 51
Supports Reproductive Health
In women, the antioxidant properties of CoQ10 protect eggs from oxidative damage. CoQ10 from food becomes even more important as you age since your body’s ability to produce the compound slows.
CoQ10 may slow and even reverse age-related egg quality and quantity decline. 13
In men, sperm is similarly vulnerable to oxidative damage, leading to lower sperm count and quality.14
Studies show that the anti-oxidant properties of CoQ10 can boost the quality, motility, and quantity of sperm.15 16
Protection Against Skin Aging
Studies show that people with low CoQ10 levels are more susceptible to developing skin cancer. 21
Other studies show that direct application of CoQ10 to the skin can reduce damage from UV rays, harmful compounds, and oxidative factors.19 20
Though you won’t be applying CoQ10 foods directly to your skin, increasing your internal CoQ10 levels may aid in protecting your skin from aging.
Reduces Migraines
CoQ10’s ability to support your cellular energy centers, the mitochondria, reduces inflammation, leading to reduced incidences of migraines.
Studies show that when compared to a placebo CoQ10 was three times more effective in reducing the number of migraines.2
Boosts Exercise Performance
Studies have found that CoQ10 can support athletic performance by protecting against oxidative stress and boosting mitochondrial functions. 30 31
Supplementing with CoQ10 has also been found to reduce fatigue and increase power during physical activity.32 33
May Protect Against Cancer
Oxidative stress can damage the structure of your cells and thereby increasing cancer risk.41
CoQ10 may protect against cancer by promoting cellular energy and reducing oxidative damage 42 43
There is also a correlation between cancer patients and low levels of CoQ10. In fact, low CoQ10 has been linked to a 53.3% higher chance of various cancers.43 44 45
The good news is that supplementing with CoQ10 has been shown to help reduce the risk of recurrence of some cancers.46
Top Foods High in CoQ10

Though numerous healthy whole foods contain CoQ10, it is impossible to consume the quantity of CoQ10 you’d get from supplements.
The standard supplement dose of CoQ10 is between 60 and 500 milligrams.
If you’re consuming a high meat keto or carnivore diet, you’d still only be able to consume around 20 or 30 mg per day for a max of 20-30% of a supplement.
Does this mean you should ignore food sources of CoQ10?
Absolutely not. Focusing on high CoQ10 foods means consuming the most nutrient-dense foods on earth, including organ meats, fresh beef, pork, fatty fish, and if you’re feeling super adventurous, reindeer meat.
These animal-based whole foods are at the center of the diets of disease-free traditional peoples, and they represent the foods that humans evolved on for nearly 2 million years.
CoQ10 foods also provide robust amounts of
- essential B vitamins,
- zinc
- selenium
- Vitamin A in its highly bioavailable form called retinol
- Vitamin K2 (an important activator of other fat-soluble vitamins)
- Healthy animal fats
- complete proteins
- Meat-specific nutrients like carnitine, creatine, and taurine
Furthermore, because CoQ10 is a fat-soluble compound, consuming it in its natural form alongside fatty whole foods can increase the rate of absorption by 300% compared to supplementing without dietary fats.2 62
Should I Supplement with CoQ10?
Supplementation with CoQ10 is considered safe and may be highly beneficial if you have any of the conditions listed above that are related to low CoQ10. 58
Since 90% of the CoQ10 in the body is in the form known as ubiquinol, this is the most popular form of supplementation.
Dr. Kiltz’s Molecular Fertility formulas offer a ubiquinol CoQ10 supplement with Vesissorb technology for improved bioavailability.
List of Top 15 Food Sources of CoQ10

Top Meat Sources of CoQ10
| Type | mg of CoQ10 per 100 g | |
| 1. | reindeer meat | 15.8 |
| 2. | pork heart | 11.8 |
| 3. | chicken liver | 11.6 |
| 4. | beef heart | 11.3 |
| 5. | chicken heart | 9.2 |
| 6. | pork shoulder | 4.5 |
| 7. | beef shoulder | 4.0 |
| 8. | beef liver | 3.9 |
| 9. | beef sirloin | 3.1 |
| 10. | beef thigh | 3.0 |
| Top Fish and Seafood Sources of CoQ10 | ||
| Type | mg of CoQ10 per 100 g | |
| 1. | herring, heart | 12.0 |
| 2. | mackerel, heart | 10.5 |
| 3. | mackerel, red flesh | 6.8 |
| 4. | herring, flesh | 1.5 |
| 5. | tuna, canned | 1.5 |
CoQ10 Foods: The Takeaway
CoQ10 is a fat-soluble compound that provides powerful anti-oxidant and mitochondria-boosting benefits.
These qualities make CoQ10 a powerful factor in supporting heart health, preventing and treating cancer, reducing migraines, supporting cognitive health, improving exercise performance, and protecting skin from UV and age-related damage.
Because CoQ10 is concentrated in vital organs, including the heart, and liver, these organ meats tend to provide the highest concentration of CoQ10. Beef, pork, and fatty fish also provide modest amounts of CoQ10.
Your body makes most of its CoQ10 on its own, so consuming it in the format of nutrient-dense whole foods is likely sufficient for most people.
However, since your ability to produce CoQ10 declines with age, taking high doses of CoQ10 in supplement form may be appropriate for some people, especially if at risk for heart conditions.
Of course, we recommend consulting with your healthcare provider regarding any kind of self-administered treatments.