We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
9 Healthiest Foods to Eat in the World: Separating Fact from Fiction

Pretty much every other list you’ll see of the healthiest foods to eat in the world are plant-based, with the lone meat being salmon. Frankly, these lists do not accord with nutritional science. They’re founded on outdated data, complex beliefs and feelings about eating animals, and the economic interests of industrial agriculture.
Table of Contents
Before launching into our science-based list of the healthiest foods to eat in the world, let’s get a few things straight:
- Fresh meat is very healthy for most people–it’s loaded with bioavailable and meat-specific nutrients, highly satiating, and associated with numerous markers of health, fertility, and longevity [1][2].
- Consumption of carbohydrate crops (grains and tubers) does not lead to greater life expectancy [3].
- Total meat consumption correlates to greater life expectancy, independent of the competing effects of total calories intake, economic affluence, urban advantages, and obesity [3].
- Saturated fat when consumed as part of a matrix of whole foods including fresh meat, is healthy for most people [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10].
- Reducing saturating animal fat and substituting in more lean protein may increase the risk of cancer [8].
- Randomized control trials comparing high-meat, low-carb diets to non-meat diets reveal dramatically better outcomes for the high-meat diets in areas of cardiovascular health, weight loss, and blood sugar regulation [8] [9] [10].
- Insoluble fiber, especially from grains, is not essential, and likely unhealthy–contributing to constipation, bloating, diverticulitis, and various other GI issues [10][11][12].
- Our human ancestors were apex predators that ate mostly fatty meat for nearly 2 million years of our evolution, suggesting that our physiology is genetically primed to thrive on meat [13].
- Meat farmed with “regenerative agricultural practices” or “carbon farming” sequesters carbon while maximizing soil health. Current industrial agricultural practices for growing plant foods will completely destroy our topsoil in 60 years [14]. When raised regeneratively, the healthiness of meat can be extended beyond the human body, to benefit our environment and food systems [15].
How we rank: Taking into account the numerous studies above, we consider only the most nutrient-dense foods. These foods are rich in complex proteins, healthy fats, bioavailable vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that your body needs to thrive. We’ve included both animal and plant food sources.
If eaten together, this list of foods will provide more than enough of all your macro and micronutrient needs.
If this isn’t the healthy food list you were expecting, it’s time to update your nutritional knowledge. Let’s dive in.
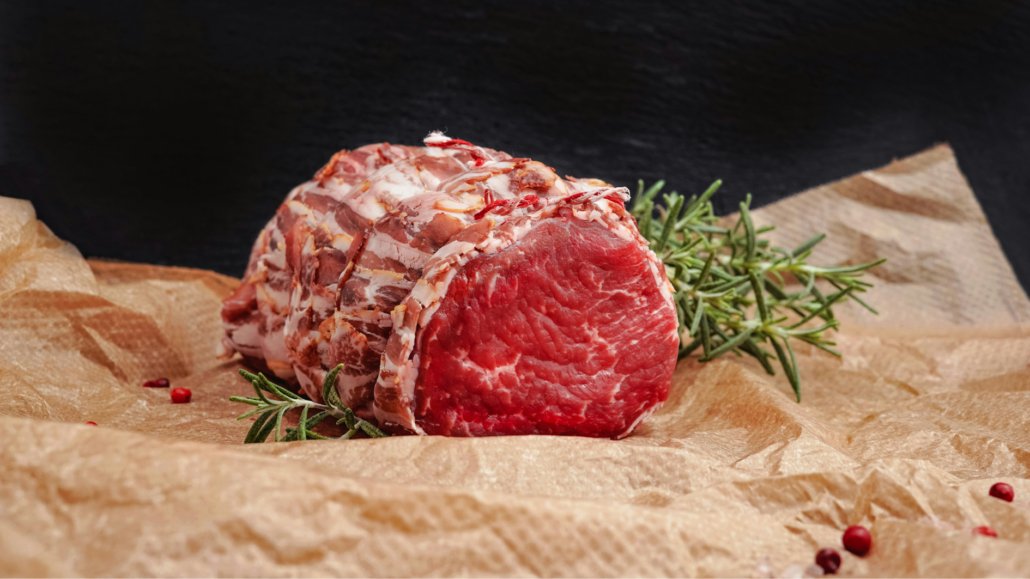
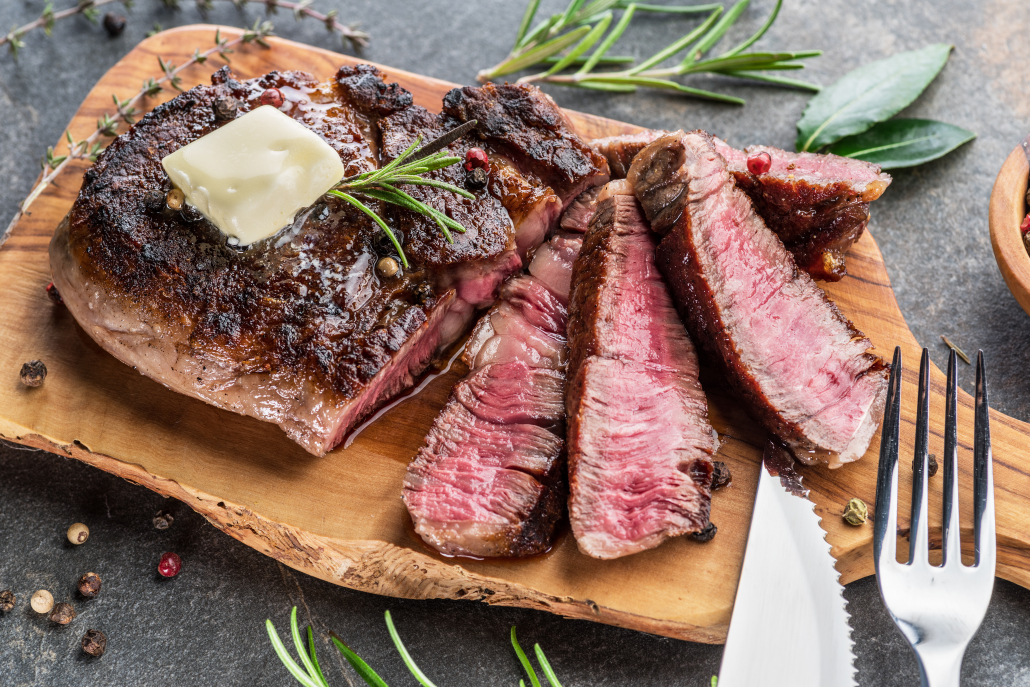
Ribeye Steak (and other fatty red meats like Brisket, Chuck, New York Strip, Denver, Short ribs, Skirt, etc)

For people who still believe in the debunked low-fat diet trend, it can be hard to fathom that this rich cut of steak headlines our list of the healthiest foods to eat in the world. But for people eating a carnivore or ketogenic diet, ribeye is the most beloved fatty keto meat.
Ribeye is so loaded with healthy fats, proteins, and essential micronutrients that you can literally thrive while eating only ribeye, salt, and water. This minimalist version of the carnivore diet is called the Lion Diet.
Ribeye (and other fatty red meats like Brisket, Chuck, New York Strip, Denver, Short ribs, Skirt, etc) are possibly the only food in the world that a human can eat singularly and not only live but thrive. It has everything you need without risks of vitamin toxicity or protein poisoning.
Researchers from Harvard University looking at 2,029 people over 6 months found that an all-meat carnivore diet found that, “Contrary to common expectations, adults consuming a carnivore diet experienced few adverse effects and instead reported health benefits and high satisfaction.”
The self-reported positive results included [14]:
- 93% improved or resolved obesity and excess weight
- 93% improved hypertension
- 98% improved conditions related to diabetes
- 97% improved gastrointestinal symptoms
- 96% improved psychiatric symptoms
These results make sense when considering the nutrient abundance of Ribeye steak and other fatty ruminant meats. Ribeye is loaded with B vitamins, zinc, selenium, and many compounds that are only found in meat:
- Carnitine: supports male fertility, mitochondrial function, supports heart health and fertility [31]
- Taurine: This antioxidant can reduce glycation, reduce oxidative stress, and improve mental health [32]
- Carnosine: Supports heart health, reduces glycation, and protects telomeres for anti-aging benefits [33]
- Creatine: improves cognition and protects against neurodegeneration. Supports athletic performance, and heart health [34]
| NUTRIENT | 200G (7 OZ) | |
| CALORIES | 582 cal | |
| FAT | 55g | |
| SATURATED FAT | 20g | |
| MONOUNSATURATED FAT | ||
| CARBOHYDRATES | 0 | |
| PROTEIN | 48g | |
| VITAMINS | ||
| B1 (THIAMIN) | 14% | |
| B2 (RIBOFLAVIN) | 35% | |
| B3 (NIACIN) | 44% | |
| B6 | 60% | |
| B12 | 245% | |
| MINERALS | ||
| MAGNESIUM | 12% | |
| POTASSIUM | 18% | |
| IRON | 31% | |
| COPPER | 33% | |
| PHOSPHORUS | 42% | |
| SELENIUM | 93% | |
| ZINC | 113% |
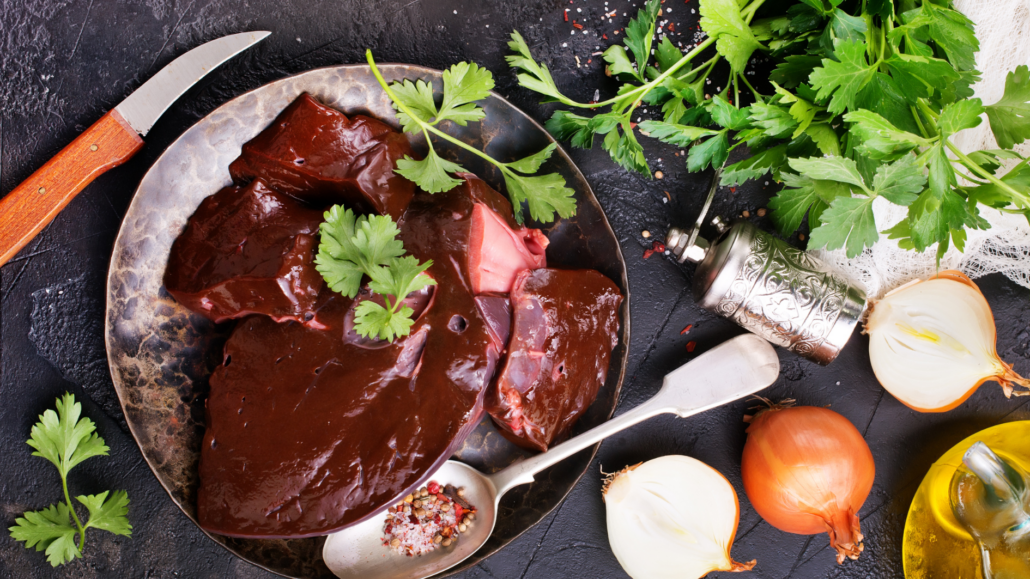
Beef Liver
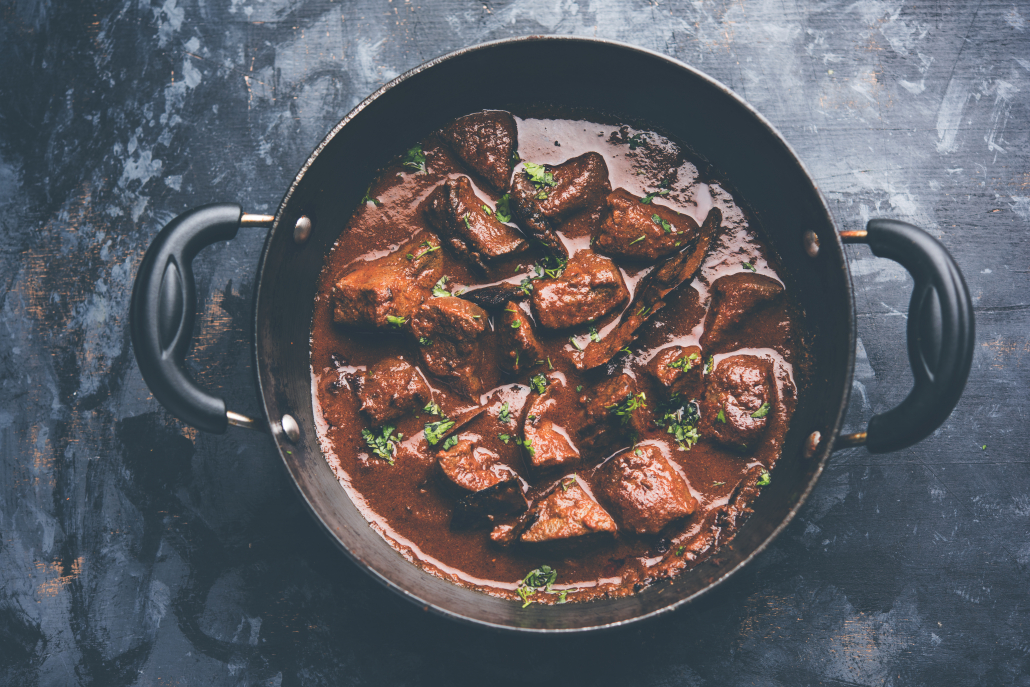

Beef liver is near the healthiest food in the world. In fact it’s so nutrient-packed that you have to eat it sparingly to protect from nutrient overload–specifically vitamin A. Just a 3.5 ounce serving 2-3 times a week will deliver all its benefits.
Vitamin A
The Vitamin A in liver comes in a variety called ‘preformed’, which is more easily absorbed and utilized in your body than the vitamin A found in plant foods. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy skin and vision [13][14].
B Vitamins and Copper
Beef liver is also loaded with B vitamins that play many roles including the metabolism of fat into energy. B vitamin combined with liver’s copious amounts of copper help maintain healthy bones, blood vessels, nerves, and immune function, and it contributes to iron absorption [15]
The folate (another B vitamin) in beef liver is critical for healthy fetal development. [16]
Heme Iron
The heme iron in liver is significantly more bioavailable than non-heme iron in plant foods [17]. It’s critical to forming red blood cells, turning food into energy, a healthy immune system, cognitive health, and fertility [18][19].
Nucleic Acids
Though not accounted for on nutrition labels nucleic acids are important nutrients that offer numerous physiological processes. Beef liver contains uniquely high amounts of nucleic acids which support: [20] [21]:
- Healthy immune function
- Digestion
- Muscle recovery
- reduced oxidative stress, inflammation
- Metabolism
Liver contains an enzyme called cytochrome P450. This compound participates in hormone production, detoxification, and the overall health of your own liver. [22]
| Beef Liver | ||
| Based on 100 grams | ||
| Calories | 135 | |
| Fat | 3.6g | |
| Protein | 20.4g | |
| Net Carbs | 3.9g | |
| Vitamins | %Daily Value | |
| Vitamin A Vitamin B6 Vitamin B12 Thiamine Riboflavin Niacin Folate Choline Vitamin C Vitamin D Vitamin K | 4968μg 1mg 59.3μg 0.2mg 2.8mg 13.2mg 290μg 333.3mg 1.3mg 1.2μg 3.1μg | 552% 84% 2471% 13% 163% 66% 73% 61% 3% 8% 3% |
| MINERALS | ||
| Iron Magnesium Phosphorus Zinc Copper Manganese Selenium | 4.9mg18mg 387mg 4mg 9.8mg 0.3mg 39.7μg | 62%6% 39% 27% 488% 16% 57% |
Oysters

Oysters are one of the healthiest foods to eat in the world thanks to a rich nutrient profile that helps:
- Reduce oxidation
- Support fertility
- Improve body composition
Many people know that oysters are high in immune-supporting zinc, with 605% per 3.5 oz serving. Lesser known is that oysters are one of hte best dietary sources of vitamin D. This makes them especially healthy for people who live in latitudes where you don’t get much sun, and during gray winter months.
The zinc, vitamin D, and selenium in oysters work synergistically to support immune function [15]. Vitamin D has been shown to help fight viral infections including COVID-19 [15][16][17].
A 3.5 ounce serving of oysters provides many hard-to-get vitamins and minerals
| RAW OYSTER CALORIES | 68 CALORIES | % RDV |
| PROTEIN | 7 grams | 8% |
| FAT | 2.5 grams | 1% |
| CARBS | 3.9 grams | 4% |
| VITAMIN D | 320 IU | 80% |
| VITAMIN B1 | 0.1 mg | 7% |
| VITAMIN B3 | 1.4 mg | 7% |
| VITAMIN B12 | 19.5 mcg | 324% |
| IRON | 6.7 mg | 37% |
| MAGNESIUM | 47 mg | 12% |
| PHOSPHORUS | 135 mg | 14% |
| ZINC | 90.8 mg | 605% |
| COPPER | 4.5 mg | 223% |
| MANGANESE | 0.4 mg | 18% |
| SELENIUM | 63.7 mcg | 91% |
Salmon Roe

Salmon roe, has long been considered one of the healthiest foods to eat in the world, even by indigenous populations who made salmon roe a part of traditional pregnancy diets.
Salmon roe provides abundant omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, critical to healthy brain function [18].
The abundance of nutrients in salmon roe including omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, along with B12, selenium, high levels of vitamin D, and E support various health goals including:
- Reduced inflammation
- Neuroprotection
- infant brain development
- Fertility for men and women
- cognitive performance
- Mood support
- heart health
- Immune function.
Salmon Roe nutrition per 100g
| NUTRIENTS | AMOUNT | |
| CALORIES | 250 kcal | |
| CARBOHYDRATE | 2.90 g | |
| FIBER | 0 g | |
| SUGARS | 0 g | |
| FAT | 14.0 g | |
| SATURATED FAT | 2.04 g | |
| MONOUNSATURATED FAT | 4.13 g | |
| POLYUNSATURATED FAT | 4.12 g | |
| OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS | 3.50 g | |
| OMEGA-6 FATTY ACIDS | 0.31 g | |
| PROTEIN | 29.20 g | |
| VITAMINS | ||
| COBALAMIN (B12) | 20.0 mcg | 333 % |
| VITAMIN E | 10mg | 66% |
| VITAMIN D | 232 IU | 58 % |
| CHOLINE | 247.5 mg | 45 % |
| PANTOTHENIC ACID (B5) | 3.50 mg | 35 % |
| VITAMIN C | 16 mg | 26 % |
| RIBOFLAVIN (B2) | 0.36 mg | 21.2 % |
| PYRIDOXINE (B6) | 0.32 mg | 16.0 % |
| VITAMIN E | 2.68 mg | 13.3 % |
| FOLATE | 50.0 mcg | 12.5 % |
| VITAMIN A | 91 mcg RAE | 10.1 % |
| THIAMIN (B1) | 0.14 mg | 9.3 % |
| Selenium | 65.5 mcg | 93.6% |
| Magnesium | 300 mg | 75% |
| Iron | 11.88 mg | 66% |
| Sodium | 1500 mg | 62.5% |
| Phosphorus | 390 mg | 39% |
| Calcium | 275 mg | 27.5% |
Dark Chocolate

Minimally processed chocolate with at least 70% cocoa can be one of the healthiest foods to eat. Its inclusion in this list of the healthiest food in the world has mostly to do with its powerful antioxidant properties combined with non-oxidizing saturated fats.
It’s worth noting that antioxidants are less important when eating a diet low in oxidizing foods. Unfortunately, the standard American diet is loaded with oxidizing added sugar and PUFA vegetable oils.
One study found that dark chocolate offered greater antioxidant activity, along with more polyphenols, and flavanols than any other tested fruits including acai and blueberries [19].
Other studies have found these antioxidant properties of chocolate to powerfully decrease oxidized (bad) LDL cholesterol. In people with high cholesterol, dark chocolate has been shown to increase HDL (good) cholesterol and decrease total LDL [20].
These positive effects on cholesterol are thanks to powerful antioxidants that enter the bloodstream where they protect lipoproteins against oxidative damage [21][22][23].
The heart-protective effects are so powerful that in a large study looking at 470 older men found that chocolate reduced the risk of heart disease by 50% over a period of 15 years [24].
While a separate study found that consuming dark chocolate at least 5 times per week lowered heart disease risk by 57% [25]. Still more studies have found that consuming chocolate at least twice per week reduced risk of calcified plaque in the arteries by 32% [26].
Chocolate is also healthy for your skin. The flavanols in dark chocolate have been shown to improve the flow of blood to the skin, increase hydration and desnity of skin, and protect against sun damage [27].
Dark Cholate Nutrients per 3.5 oz.
| Nutrients | Amount | |
| Fat | 31.2 g | |
| Saturated fat | 18.6 g | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 9.5 g | |
| Carbohydrates | 59.5 g | |
| Fiber | 7 g | |
| Protein | 4.9 g | |
| Iron | 8 mg | 46% |
| Potassium | 555 mg | 12% |
| Caffeine | 42.7 mg |
Avocados
Avocados are high in both macro and micronutrients that many people eating modern Western diets lack. On a ketogenic diet avocados are one of the few low-carb foods high in potassium and vitamin C.
Avocados are a good source of many B vitamins, including folate. Folate plays a key role in the production of red and white blood cells in bone marrow, DNA and RNA, and fetal development [27]
For people practicing vegan or vegetarian keto, avocados are an important staple. However, since avocados are a plant food with plant toxins, some people do have mild to severe allergies [*][*]
The potassium in avocados is essential for nervous system function and blood pressure regulation, and protective against stroke and hypertension [28][29].
A study showed that eating the equivalent of 1 avocado a day for 12 weeks lowered concentrations of fecal bile acid while increasing the diversity of healthy gut bacteria [30].
Nutrients in a medium Hass avocado
| Nutrients | |
|---|---|
| Calories | 322 |
| Fat | 30 g |
| Protein | 4 g |
| Carbohydrates | 17 g |
| Fiber | 14 g |
| Vitamin C | 22% |
| Vitamin E | 28% |
| Vitamin K | 35% |
| B2 | 20% |
| B3 | 22% |
| B5 | 56% |
| B6 | 30% |
| Folate | 41% |
| Magnesium | 14% |
| Potassium | 21% |
| Copper | 42% |
| Manganese | 12% |
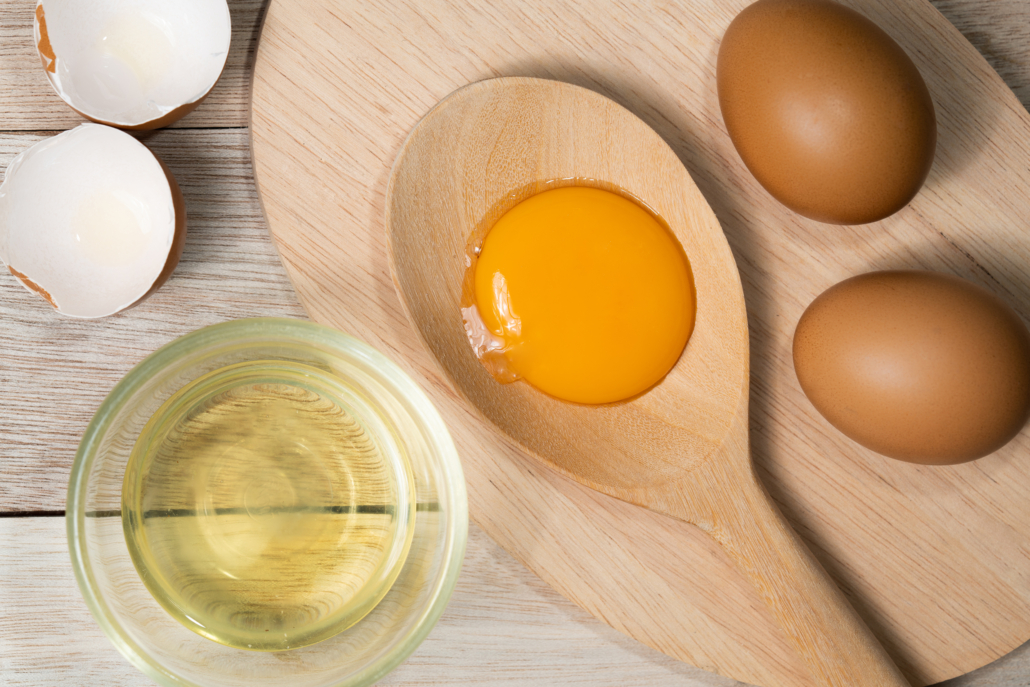
Eggs
Eggs contain all the nutrients–healthy fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals– needed to grow an entire animal, so it’s no wonder that they’re one of the healthiest foods to eat in the world.
A nutrient highlight is an egg’s choline content. Your body needs choline to produce the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is crucial for memory, mood, and intelligence. Choline also plays a key role in synthesizing DNA, which is especially important for infant brain development [35].
| Nutrients | 100 grams (appx 2 eggs) | %Daily Value |
| Calories | 140 | |
| Fat | 10 | 16% (Not on Ketogenic Diet |
| Protein | 12 | |
| Vitamins and Minerals | ||
| Retinol (vitamin A) | 98mcg | 12% |
| Riboflavin | 0.4mg | 33% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.33mcg | 100% |
| Biotin | 5.2mcg | 17% |
| Folate | 88mcg | 30% |
| Vitamin D | 7.9mcg | 30% |
| Vitamin E | 1.9mg | 30% |
| Pantothenic acid | 1.07mg | 22% |
| Phosphorus | 171mg | 25% |
| Iron | 1.8mg | 23% |
| Selenium | 28mcg | 50% |
| Choline | 164mg | 38% |
| Zinc | 1.0mg | 10% |
| Iodine | 47mcg | 33% |
Anchovies
These little fish are indeed one of the healthiest foods to eat in the world, thanks to their combination of healthy fats, abundant protein, and complex of micronutrients.
The B3 in anchovies is crucial for converting food into usable energy. The very high levels of selenium support heart health and thyroid function [48] [49]
Anchovies are fatty fish offering more omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) than nearly every other fish, including the much-lauded salmon.
The high selenium and Omega-3s in anchovies can help prevent tumor growth and is used to treat various types of cancer [50] [51] [52].
| Anchovies (Wild) | Amount per 3 oz. | % RDA |
| Fat | 15.9g | |
| Saturated Fat | 128g | |
| Cholesterol | 61mg | |
| Protein | 28g | |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin D | 103.5IU | 16.5% |
| Vitamin K | 18µg | 15% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.4µg | 56% |
| B3 | 30mg | 186% |
| B6 | .3mg | 24% |
| B2 | .6mg | 42% |
| B5 | 1.4mg | 27% |
| Choline | 128mg | 23% |
| Significant Minerals | ||
| Selenium | 102µg | 186% |
| Zinc | 3.6mg | 26% |
| Potassium | 816mg | 21% |
| Calcium | 348mg | 38% |
| Iron | 6.9mg | 39% |
| Copper | .4mg | 57% |
Beef Kidney

Beef kidney is another organ meat that makes the list of the healthiest food to eat.
Let’s start with anchovie’s tremendous concentration of B12, which is over 1000% per 100-gram serving.
Kidney also offers the rare, organ-specific amino acid L-ergothioneine that directly supports the health of your own kidneys [53].
This superfood provides another rare amino acid called ergothioneine, which supports fertility [54].
Kidney is also prized for the saturated fat encasing it, called suet [55]. high in stearic acid, suet can help reduce body fat and improve mitochondrial function [56].
| Beef Kidney: Raw | ||
| Based on 100 grams | ||
| Calories | 99 | |
| Fat | 3.1g | |
| Protein | 17.4g | |
| Net Carbs | 0.3g | |
| VITAMINS | %Daily Value | |
| Vitamin AVitamin A IU Thiamine Riboflavin Niacin Folate Vitamin B6 Vitamin B12 Vitamin C Vitamin D Vitamin E | 419μg1397IU 0.4mg 2.8mg 8mg 98μg 0.7mg 27.5μg 9.4mg 1.1μg 0.2mg | 47%– 24% 168% 41% 25% 52% 1146% 16% 8% 2% |
| MINERALS | ||
| CalciumIron Magnesium Phosphorus Zinc Copper Manganese Selenium Retinol Lycopene | 13mg4.6mg 17mg 257mg 1.9mg 0.4mg 0.1mg 141μg 419μg 20μg | 2%58% 5% 26% 13% 22% 8% 202% – – |
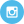
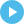
What About Kale?
Most people think of kale as extremely healthy due to its vitamin and mineral content, but in fact, Kale pales in comparison to every food on our list.
See for yourself how kale stacks up against eggs below.
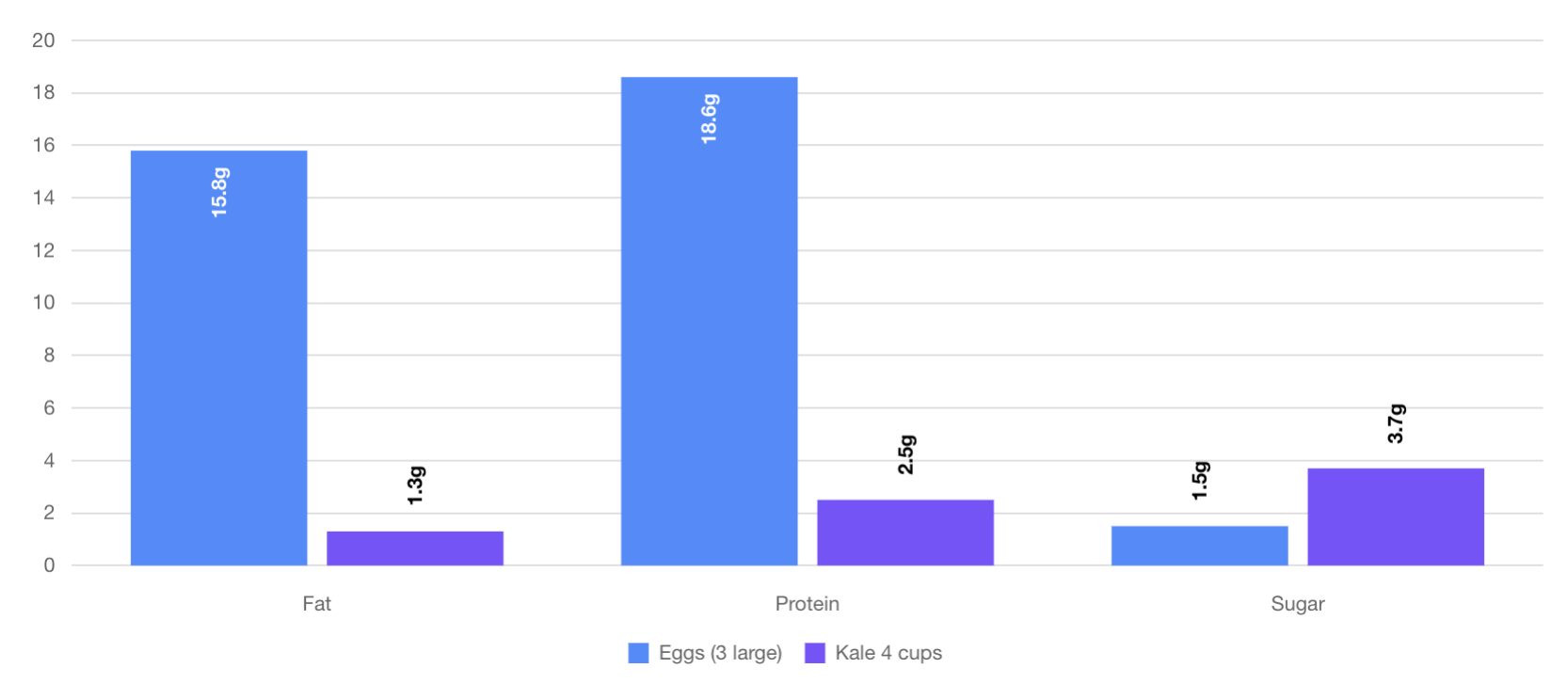
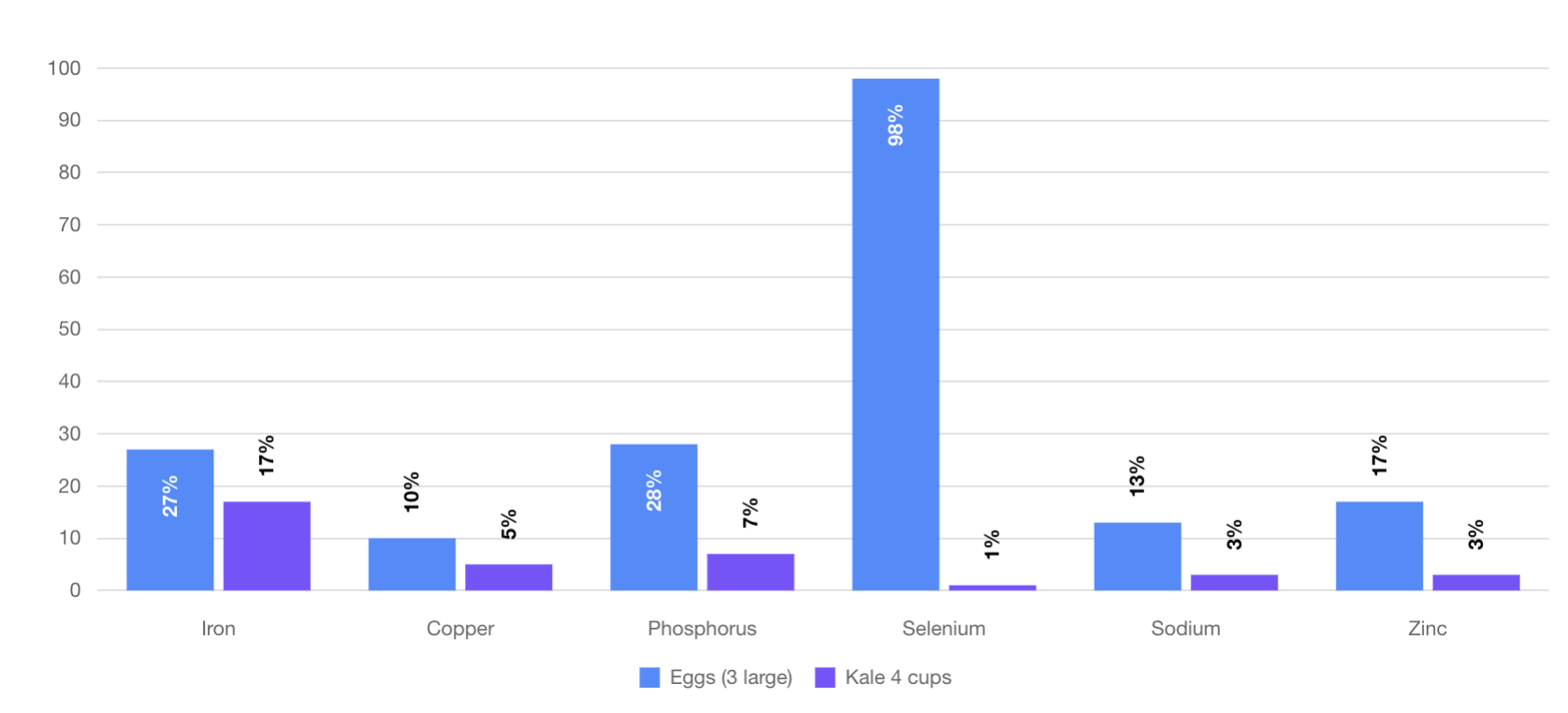
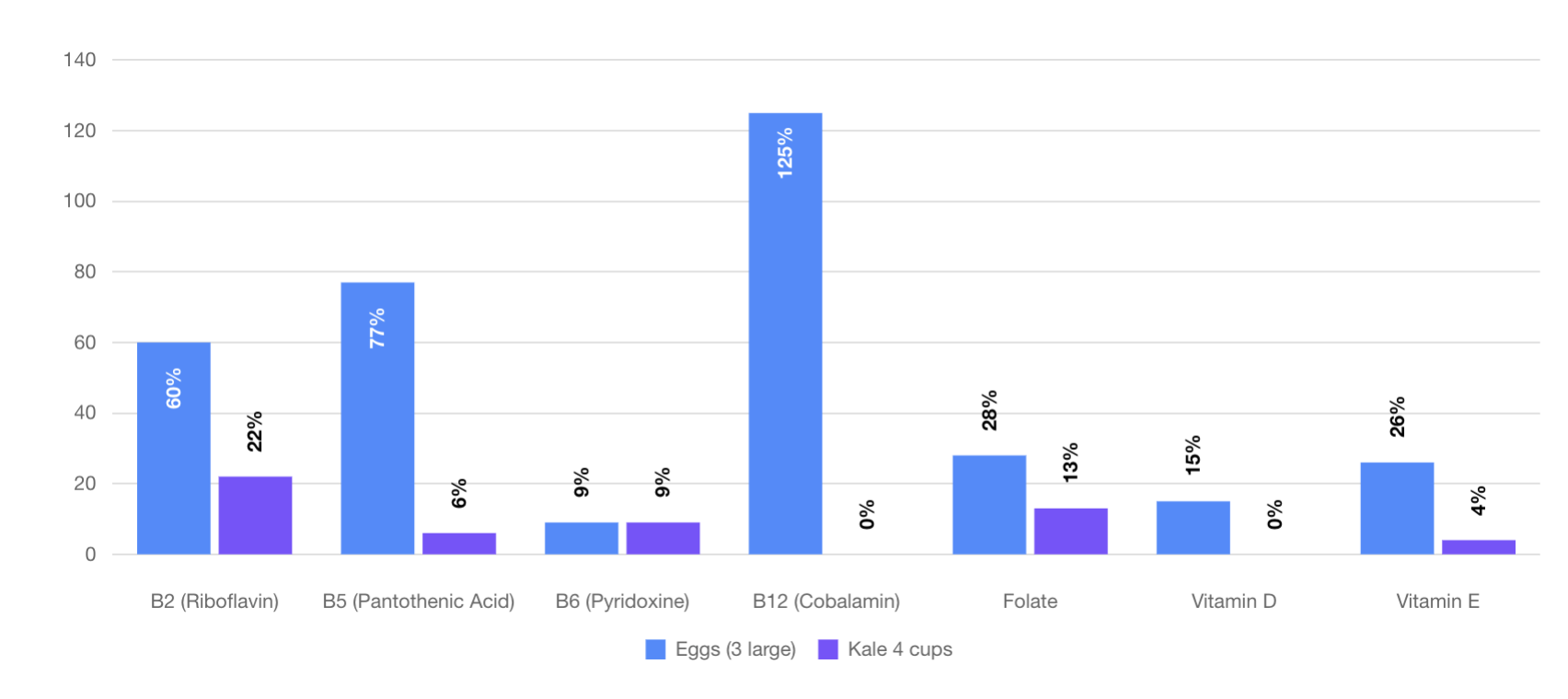
routinely shows up o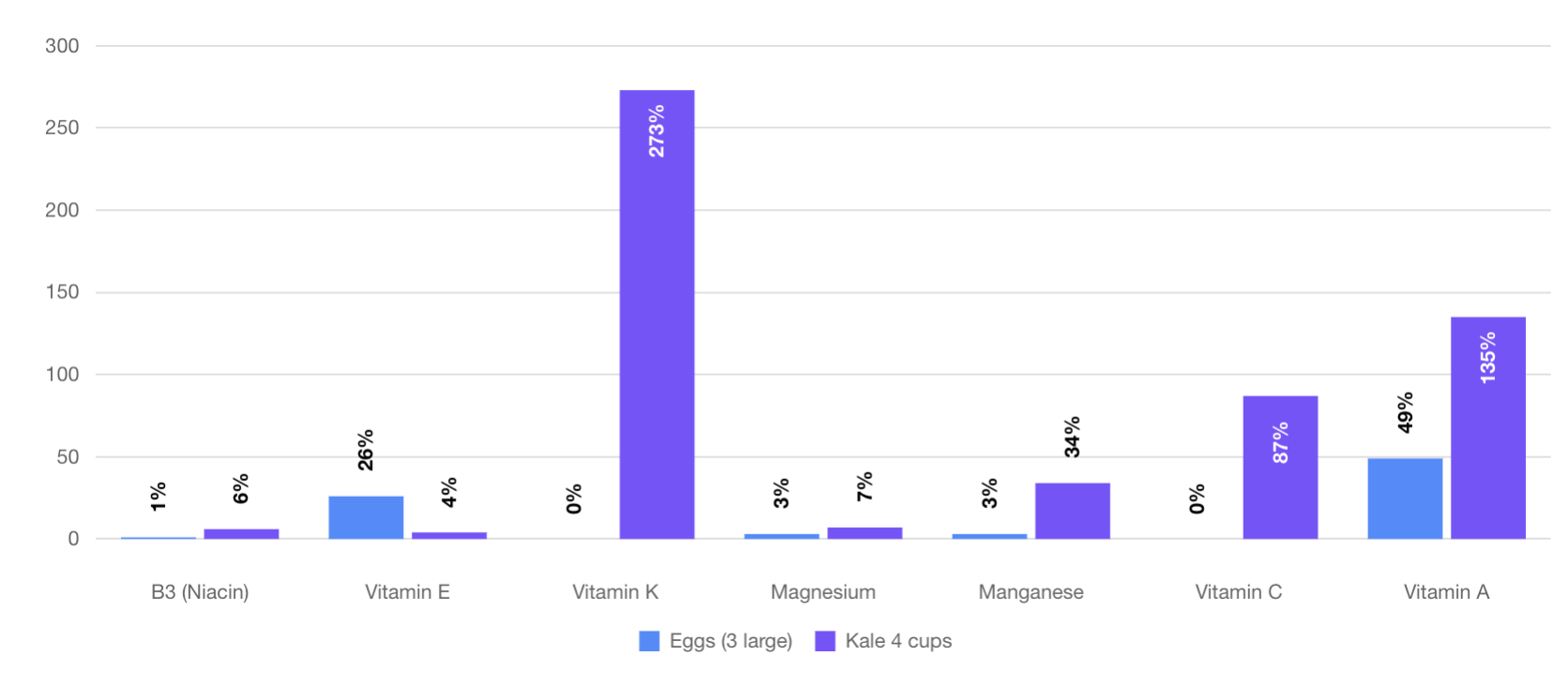
As you can see, eggs are far more nutritious.
Interestingly, even the nutrients like Vitamin A and Vitamin K, in which Kale famously shines, have some very important caveats.
Vitamin K which Kale appears to be loaded in is specifically Vitamin K1. Research is now showing, however that Vitamin K1, which is found in plant sources like Kale, is inferior to Vitamin K2 which is found in meats and cheese.
Similarly, 4 cups of Kale has 135% of your “vitamin A” which appears to be better than the 49% found in 3 large eggs. But that’s not the whole story. Vitamin A found in plant foods isn’t even vitamin A, it’s Beta Carotene, a vitamin A precursor. Vitamin A found in animal-based foods like eggs is already in its preformed, bioactive state and is much easier to absorb.
According to various studies, Preformed Vitamin A, Retinol, absorption efficiency ranges between 75% and 100%. On the other hand, studies show that the absorption efficiency of β-carotene may be as little as 3%, ouch!
Additionally, Kale appears on the Environmental Working Group’s “Dirty Dozen” list of vegetables to be avoided.
When tested, 92 percent of kale had high levels of residue from at least two pesticides that are carcinogenic, even after washing.
The Healthiest Food to Eat in the World: The Takeaway
Contrary to popular belief the healthy food to eat in the world isn’t plant-based. Rather, these foods are mostly whole animal foods, replete with healthy fats, protein, and complex blends of essential micronutrients.
These views are reflected in the eons-old eating patterns of traditional cultures. Pioneering researcher Dr. Weston Price tracked the robust health of traditional cultures to the foods they ate–specifically nose-to-tail animal-based foods rich in fat-soluble activator vitamins A, D, and K2.
He found that traditional diets centered around many of the foods on this list contained 400% more water-soluble vitamins and 1000% more fat-soluble vitamins than the Standard American Diet of his time.