We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
The Low Carb High Fat Diet: A Complete Guide for Beginners

Low-carb, high-fat (LCHF) diets have been shown to be effective in combating numerous disorders, including metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, acne, PCOS, and neurological issues such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease [1].
For these reasons, LCHF diets have seen a boom in popularity over the last decade. LCHF diets may finally be putting the nail in the coffin of the bogus low-fat high-carb diet trends that have unfortunately persisted since the 1990s.
In this article, we’ll explore various types of low-fat, high-carb diets and their health benefits, along with lists of LCHF foods to eat.
Table of Contents
What is a Low-Carb High-Fat Diet?
High-fat low-carb eating means significantly reducing carbs and replacing them with high-fat whole foods.
There are many variations of high-fat, low-carb ways of eating, with carb intake ranging from 10-100 grams per day.
Most HFLC eating protocols call for eliminating processed foods, sugar, grains, pasta, bread, rice, and legumes.
Most LCHF diets revolve around:
- Red meat
- Pork
- fatty fish
- Fatty seafood
- Eggs
- Butter
- Other healthy fats like lard and ghee
Benefits of Low-Carb High-Fat Diets
There are numerous benefits of LCHF diets, including
- Combating carb addiction
- Protection against diabetes
- Neurological protection
- Protection against heart disease
- Loss of excess weight
Let’s take a closer look at the science supporting each of these benefits.
LCHF Diets Combat Carb Addiction
Well-formulated LCHF diets eliminate most carbs and replace them with far more satiating whole foods loaded with fats and proteins.
A 2011 study found that people who practiced a very low-carb, high-fat (VLCHF) diet had significantly reduced cravings for carbs compared with people eating a low-fat diet [11].
The LCHF diet may be a particularly helpful tool for those whose weight-loss goals are sabotaged by strong cravings for carbohydrates.
Additionally, the LCHF group had significant reductions in all-around hunger compared with the low-fat group [12].
Diabetes
A 2015 study found that when comparing low-carb, high-fat diet with a high-carb diet, participants on the LCHF diet showed greater blood sugar control and significant reductions in the use of diabetes medications [13].
Another study looking at obese people with type 2 diabetes similarly found that a very low-carb, high-fat ketogenic diet resulted in significant blood sugar control and medication use reduction. With some participants discontinuing use of their medications [14]
A 2011 pilot study looked at the effects of an LCHF diet called the “Spanish Keto Mediterranean Diet” on 22 participants with metabolic syndrome–a precursor to diabetes.
After 12 weeks researchers found that for all 22 participants [15]:
- Fasting blood sugar levels dropped from a pre-diabetic 118 to an ideal 91
- Subjects lost an average of at least 30 pounds
- All participants no longer had metabolic syndrome
- They lost an average of 6 inches (16 centimeters) from their waist
- Body mass index (BMI) dropped from 37 to 31.5: This represents a change from class 2 obesity to the low end of class 1
- An increase in “good” HDL cholesterol from 44 to 58
- A decrease in triglycerides from 224 to 109
- A change from “prehypertensive” to “normotensive”
- Markers for fatty liver disease, including liver enzymes and liver fat reduced, and in some cases completely resolved
LCHF for Neurological Protection
The ketogenic LCHF diet entered mainstream medicine over 100 years ago as a treatment for epilepsy that could not be remedied with drugs [16].
It’s no surprise that the neuroprotective abilities of LCHF diets have been shown to be effective in other areas. One study found that keto can improve cognitive function for people with Alzheimer’s disease and limit the progression of the disease.
Studies show that LCHF diets may play a therapeutic role in other neurological diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease [17].
The neuroprotection provided by LCHF diets likely has to do with dramatically reducing sugar. Research shows that chronically high consumption of carbs and added sugars is linked with cognitive decline, while LCHF diets have been linked with improvements in cognitive function [18][19].
LCHF Supports Heart Health
LCHF diets positively affect numerous markers of heart health, including:
- Reduced body fat
- Reduced inflammation
- Blood lipid markers
A 2014 study looking at a 12-week LCHF diet on 55 obese adults found that it reduced triglycerides and improved HDL cholesterol while reducing levels of the inflammation marker C-reactive protein [20].
Combats Obesity
Numerous studies have found that low-carb, high-fat diets effectively support the shedding of excess weight [2][3][4][5].
Though having fat stored on the body is natural and healthy, it can also be associated with metabolic disorders and type-2 diabetes.
LCHF diets have been shown especially effective at reducing fat stored on the belly. This is important because excess belly fat is closely associated with diabetes, various cancers, and heart disease [5][6].
The factors that contribute to weight loss with LCHF diets include improved insulin sensitivity, stimulation of ketosis, and suppressing appetite with highly satiating foods [7][8].
LCHF diets have also been shown effective in keeping weight off in the long term. One 2013 review of various studies found that keeping carbs below 50 grams per day offered much greater long-term weight loss than low-fat diets [9].
A 2014 study looking specifically at the LCHF ketogenic diet found that 88% of the obese participants lost more than 10% of their body weight. The weight loss persisted for at least a year [10].
Types of Low-Carb High-Fat Diets
There are numerous types of low-carb, high-fat diets. Some have recognizable brand names like Atkins and Paleo Diet. Others are up and coming like the carnivore diet, and the minimalist Lion Diet.
Atkins
The Atkins diet was one of the first LCHF diets to hit the mainstream when Dr. Atkins wrote the book on it in 1972.
The Atkins diet begins with a two-week period where carbs are restricted to 20 grams per day. After the initial phase, you can slowly increase your carb intake.
Though originally demonized for allowing high amounts of saturated fats, the diet has since been vindicated by modern science, showing that saturated fat is not harmful [21][22].
Studies looking at the effectiveness of the Atkins diet have found that it results in greater weight loss, reductions in blood sugar, increases in HDL ‘good’ cholesterol, and various other health markers than low-fat diets [23][24].
Though Atkins limits grains, legumes, and higher-carb fruits and veggies in the “induction” phase, practitioners can re-integrate these foods later on. This can lead to relapses of carb addiction while subjecting dieters to plant toxins and antinutrients like lectins, oxalate, phytohormones, and phytoalexins.
Paleo
The paleo diet is an attempt at aligning our modern eating patterns with the ancestral foods humans evolved on during the Paleolithic era. This means gutting out grains, legumes, some industrial oils, and processed sugars.
The paleo approach is supported by the fact that at least 70% of modern foods are products of the agricultural revolution which began only 10,000 years ago [1]. In contrast, the paleolithic period with its specific selection of foods lasted nearly two million years.
Though Paleo can be formulated into an LCHF diet, it is often practiced as a diet that is moderately low in carbs and fat, and high in protein.
The foods central the paleo include:
- Meat and fish (often lean)
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Specific fats and oils, including coconut oil, olive oil, avocado oil, lard, tallow, ghee/butter
- Some raw sweeteners, including raw honey, maple syrup, coconut sugar, raw stevia
Critique of Paleo
When considering that many of the foods on paleo, including coconut oil, olive oil, avocado oil, and most fruits and vegetables, were not part of the paleolithic diet, the term Paleo is better understood as a marketing ploy.
For our ancestors, nuts and seeds were rare and required a lot of energy to process and remove poisons. It was also during this time that large animals (megafauna) were abundant.
Therefore, It’s far more likely that our paleolithic cavemen ancestors ate a diet centered on fatty meat [25]. For the above reasons, many argue that Paleo is less healthy than keto.
Keto
The ketogenic diet (keto) is a high-fat low-carb, moderate-protein diet.
This way of eating triggers your body to produce higher levels of energy molecules called ketones. When this happens you are in ketosis.
In contrast, the standard American diet is high in starch and sugar. The average American consumes 50%-60% of calories from carbohydrates, 20% of which come from added sugars [26].
There are numerous types of keto, including pescatarian keto, vegetarian keto, and even vegan keto. There is also a paleolithic keto that increases fat and restricts carb while sticking to paleo foods.
However, most experts agree that the most well-formulated keto diet is centered on fatty animal meats with limited supplementation of low-carb keto fruits and keto vegetables. There is also a growing number of keto experts supporting the carnivore diet–an all-meat version of keto.
Keto Macros
Most keto diets call for the following keto macro percentages:
- 70-80% of calories from fat
- 15-30% calories from protein
- 0-10% calories from carbohydrate
Keto has been shown to offer various health benefits that align with other LCHF diets, including [2][3][4][5]:
- Reducing and reversing diabetes
- Reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
- Reduced epileptic symptoms
- Weight loss
- Resetting gut microbiome
- Useful against specific cancers
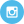
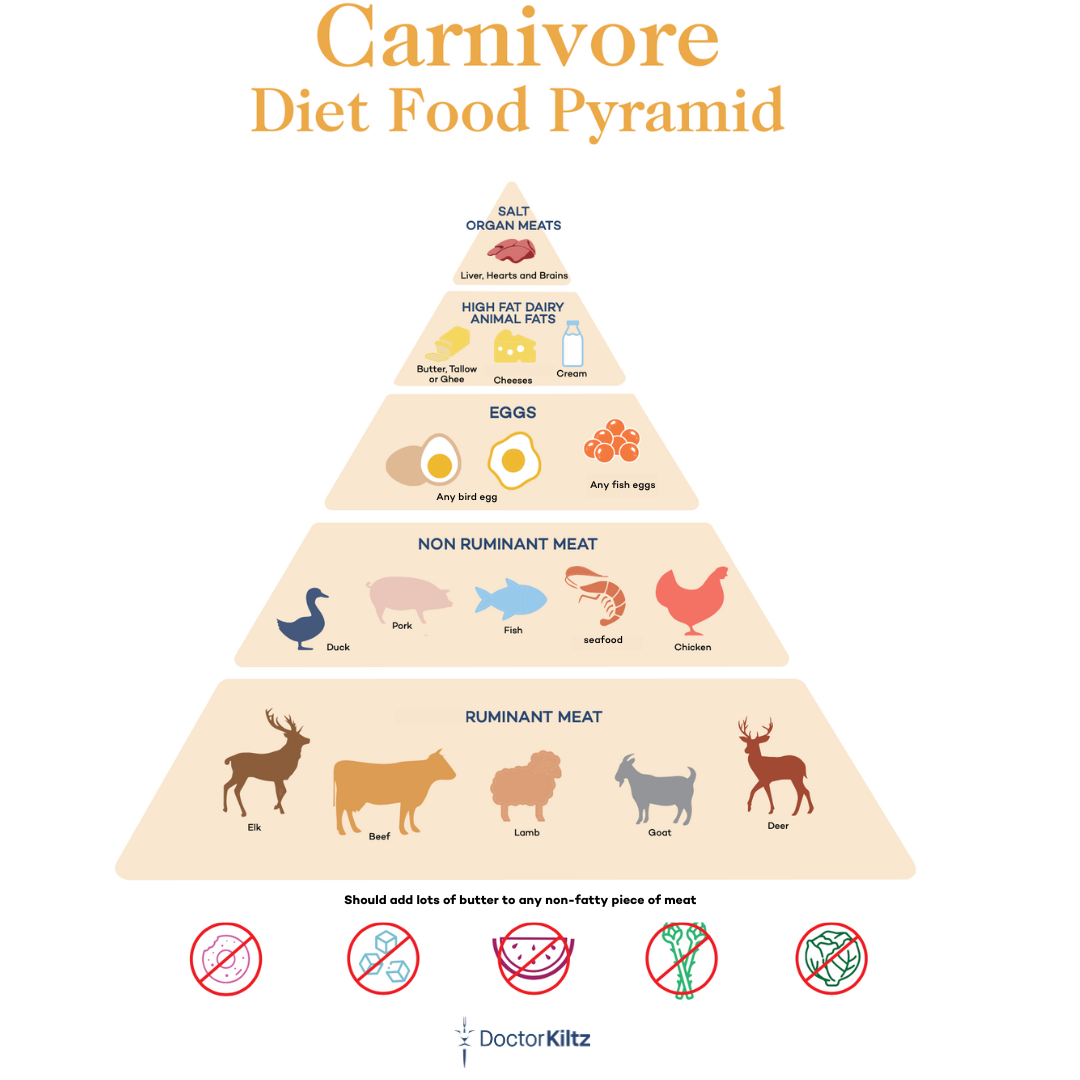
Carnivore
The Carnivore Diet is a type of high-fat low-carb diet that calls for eating only meat and animal products.
The carnivore diet is inspired by research showing that for most of the 2 million years of human evolution, our species were apex predators that ate mostly meat [3].
As a version of the keto diet, the Carnivore diet likely provides similar science-backed benefits, including weight loss, reduced inflammation, neurological protection, protection against diabetes, and protection against various inflammatory disorders.
A 2021 Harvard study looked at the effects of the carnivore diet on more than 2,000 people over six months. The Harvard researchers concluded, “Contrary to common expectations, adults consuming a carnivore diet experienced few adverse effects and instead reported health benefits and high satisfaction” [26].
Results from the study showed:
- 93% improved or resolved obesity and excess weight
- 93% improved hypertension
- 98% improved conditions related to diabetes
- 97% improved gastrointestinal symptoms
- 96% improved psychiatric symptoms
Key factors in these benefits include:
- Eliminating processed foods loaded with sugars and irritating additives
- Eliminating grains, legumes, and starches that contain lectins, phytohormones, phytoalexins, and numerous other plant defense mechanisms
- Reducing fiber. Excess fiber ferments in the gut resulting in excess heat, inflammation, constipation, diverticulitis, and IBS
- Eliminating most inflammatory polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) found in seed oils
- Consuming more monounsaturated and saturated fats from animal foods
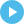
- Eating more of the healthiest food in the world, like fatty cuts of steak, nutrient-dense superfoods including beef liver, salmon roe, and organ meats
Explore more by checking out carnivore diet meal plans, and a comprehensive carnivore diet food list.
Dr. Kiltz’s Three Pillars of Health and Wellness
Dr. Kiltz’s three pillars of health and wellness takes LCHF eating a step further by incorporating diet with other lifestyle principles. Dr. Kiltz’s approach to wellbeing is based on three pillars:
- Eating high-fat low-carb whole foods–ideally, foods only found on a carnivore diet food list with some wiggle room for french fries and low-sugar keto ice cream
- Intermittent feasting (AKA intermittent fasting)–ideally one meal a day (OMAD)
- Regulating the nervous system with mindfulness meditation, positive psychology, and low-impact and restorative movement
High-fat Low-Carb foods
Well-formulated high-fat, low-carb diets are based on whole-food animal products and eliminate all industrial oils, grains, legumes, and added sugars.
Let’s look at some of the staples.
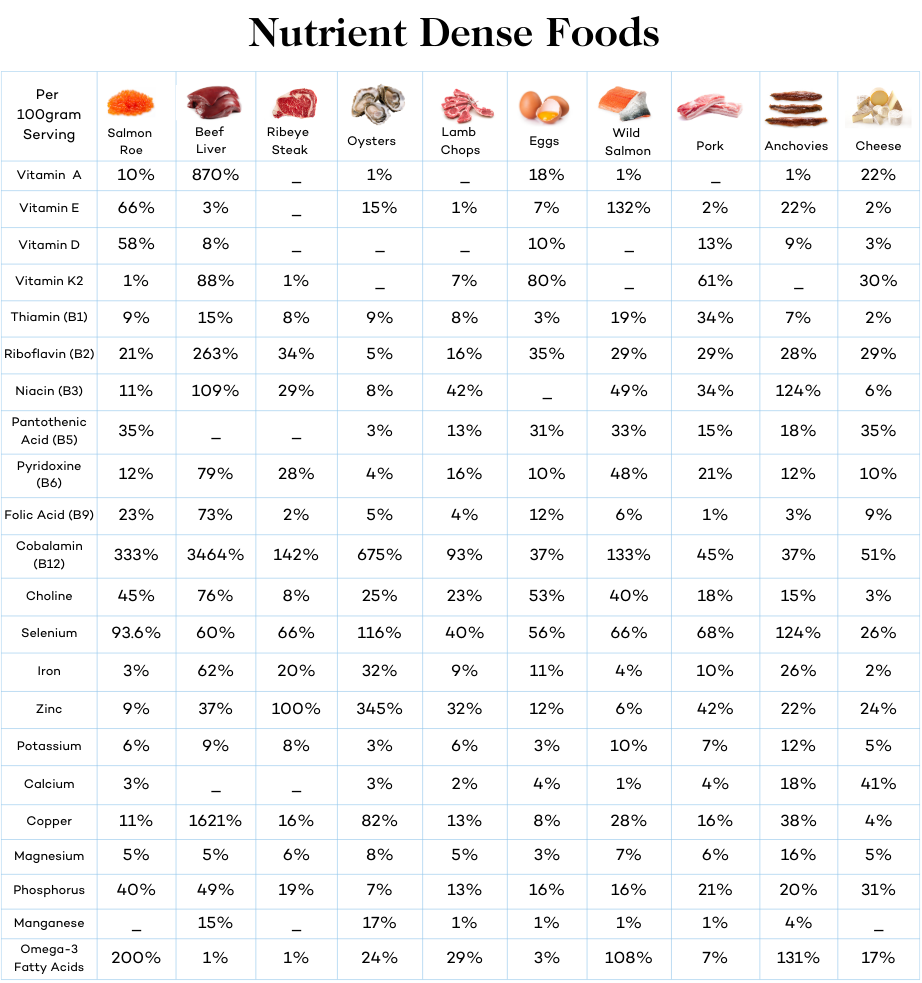
LCHF Meats
Beef, lamb, bison, and elk are all ruminant meats loaded in healthy fats and nutrients found only in meat.
Fatty Cuts of Steak Nutrition Info per 4 oz.
| Beef | Calories | Fat | Protein | Carbs | % Calories from fat | % Calories from protein | |
| #1 | Boneless short ribs | 440 | 41 | 16 | 0 | 84 | 15 |
| #2 | Tri-tip roast | 340 | 29 | 18 | 0 | 77 | 21 |
| #3 | Beef Back Ribs | 310 | 26 | 19 | 0 | 75 | 25 |
| #4 | Ribeye | 310 | 25 | 20 | 0 | 73 | 26 |
| #5 | Porterhouse | 280 | 22 | 21 | 0 | 70 | 30 |
| #6 | Top Sirloin | 240 | 16 | 22 | 0 | 60 | 37 |
| #7 | 80/20 Ground Beef | 307 | 19.6 | 30.5 | 0 | 59 | 41 |
| Lamb | Calories | Fat | Protein | Carbs | % Calories from Fat | % Calories from protein | |
| #1 | Chop/Rack | 330 | 22 | 30 | 0 | 63 | 37 |
| #2 | Loin Chop | 330 | 22 | 30 | 0 | 63 | 37 |
| #3 | Leg | 292 | 18.7 | 29.3 | 0 | 59 | 41 |
| #4 | Shank | 276 | 14.7 | 32 | 0 | 52 | 48 |
| #5 | Shoulder | 148 | 6 | 22.8 | 0 | 37 | 63 |
Pork is high in fat, protein and B vitamins. But since the fat in pork stores the fats it eats, look for pastured pork when possible. Pork raised on feed high in omega-6 can pass the imbalance along to you.
LCHF Pork Nutritional information per 4 oz.
| Pork | Calories | Fat | Protein | % Calories Fat | % Calories Protein | |
| #1 | Pork Belly | 588 | 60 | 10.4 | 92 | 7 |
| #2 | Baby back ribs | 315 | 27 | 18 | 77 | 23 |
| #3 | Pork Hocks | 285 | 24 | 17 | 76 | 24 |
| #4 | Shoulder | 285 | 23 | 19 | 73 | 27 |
| #5 | Bacon | 600 | 47.2 | 41.9 | 71 | 28 |
| #6 | Butt | 240 | 18 | 19 | 68 | 32 |
| #7 | Leg Ham | 305 | 20 | 30.4 | 59 | 40 |
LCHF Poultry
Though not as nutritious or nourishing as other HFLC meats, poultry can have a place in your diet regimen. And there’s one type of poultry that’s always encouraged: chicken liver.
Below is a list of the best LCHF poultry:
| Poultry | Calories | Fat | Protein | Carbs | % Fat | % Carbs | |
| #1 | Goose | 340 | 24.9 | 28.5 | 0 | 66 | 34 |
| #2 | Game Hen | 220 | 16 | 19 | 0 | 65 | 35 |
| #3 | Chicken Wings | 320 | 22 | 30.4 | 0 | 62 | 38 |
| #4 | Chicken thigh (skin on) | 275 | 17.6 | 28.3 | 0 | 58 | 41 |
| #5 | Duck | 228 | 13.9 | 26.3 | 0 | 55 | 46 |
| #6 | Chicken Leg (skin on) | 275 | 15.2 | 29.4 | 0 | 54 | 46 |
LCHF Fats
For most people starting out on a low-carb, high-fat diet, cutting carbs is the easy part. But getting enough fat can be a challenge when you’re not used to it. Adding a couple of tablespoons from the healthy fats below to most meals will help you meet your macro goals.
| TYPE | SFA% | PUFA % | CARBS | TOTAL FAT | NOTES |
| BEEF TALLOW | 49.8 | 3.1 | 0g | 12.8 | Mild beef flavor Can be heated |
| LARD | 41 | 12 | 0g | 13g | Mild flavor Can be heated |
| BUTTER | 50 | 3.4 | 0g | 12g | Mildly Sweet Lower Heat |
| GHEE | 48 | 5 | 0g | 9g | Mild nutty flavor Can be heated |
| DUCK FAT | 25 | 13 | 0g | 13g | Rich Duck flavor Can be heated |
| HEAVY CREAM | 62 | 4 | .5g | 5.4 | Sweet and rich |
Fruits and Veggies
Some experts like Dr. Kiltz recommend limiting all plant foods including fruits and veggies. However, if you are to eat fruits and veggies on a low-carb, high-fat diet, the following lists of low-carb options can help.



Foods to Avoid and Limit on an LCHF diet
Foods to avoid on an LCHF diet include:
- Grains and starches: Pasta, bread, rice, cereal etc.
- Sweeteners: Added sugar, honey, agave, etc.
- Carby vegetables: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, sweet squash, etc.
- Limit fruits. Consume only small amounts of low-carb fruits like berries
- Beer, mixed cocktails, and sweet wines
- Processed, packaged foods
Low-Carb High-Fat Diets: The Takeaway
Low-carb, high-fat diets present a radical break from the low-fat diet trends that have dominated modern nutrition for decades.
LCHF diets offer numerous well-researched health benefits stemming from weight loss, hormone rebalancing, and the elimination of inflammatory carbohydrates, industrial oils, and plant toxins.
There are numerous types of low-carb, high-fat diets that can be tailored to most people’s metabolic needs and activity levels.