We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Boosting Your Natural Fertility: The Essential Guide for Women and Men

Table of Contents
Have you been trying to get pregnant on your own and it’s just not working? It might be time to try a new approach specifically designed to increase your fertility the natural way.
In this article we’ll explore over 20+ natural fertility boosters, including simple dietary changes, supplements, and lifestyle additions. Keep reading to learn how you can maximize your body’s fertility naturally.
** While this article focuses on natural fertility, the natural fertility boosters mentioned here can also be applied to your IUI or IVF treatment. That’s because natural fertility boosters improve the very same egg, sperm, and uterine health that practically all fertility treatments rely upon.
Natural Conception: Optimizing Intercourse
You probably had sex-ed class back in your school days, but for better or worse most of its contents focused on preventing pregnancy. Now that your goals are different and you’re having sex specifically to get pregnant, it may be a good idea to give yourself a little refresher course.
The Fertile Window
Women can only become pregnant during a small segment of the menstrual cycle known as the “fertile window.” Timing this window right requires understanding your menstrual cycle since no two women’s cycles are exactly the same. Your body’s fertility window depends on the duration of your menstrual cycle.
Day 1: First day of your period
Days 1-14: Follicular phase
Day 14: Ovulation
Day 14-28: Luteal phase
The menstrual cycle begins with the first day of your period — that’s day 1. The following 2 weeks (days 1 through 14) of your cycle are referred to as the follicular phase. During the follicular phase, your body focuses on egg growth, maturation, and preparation of the womb.
Next comes the luteal phase, which begins when women ovulate and release an egg — this happens around day 14. From this point forward, fertilization can occur. After an egg is ovulated it has to be fertilized within 12 to 48 hours.
Since eggs have a short fertilization window and sperm have to swim such a long distance, it’s best to have intercourse right before ovulation. Timing things this way provides sperm with the best chance of reaching an egg and fertilizing it in time.
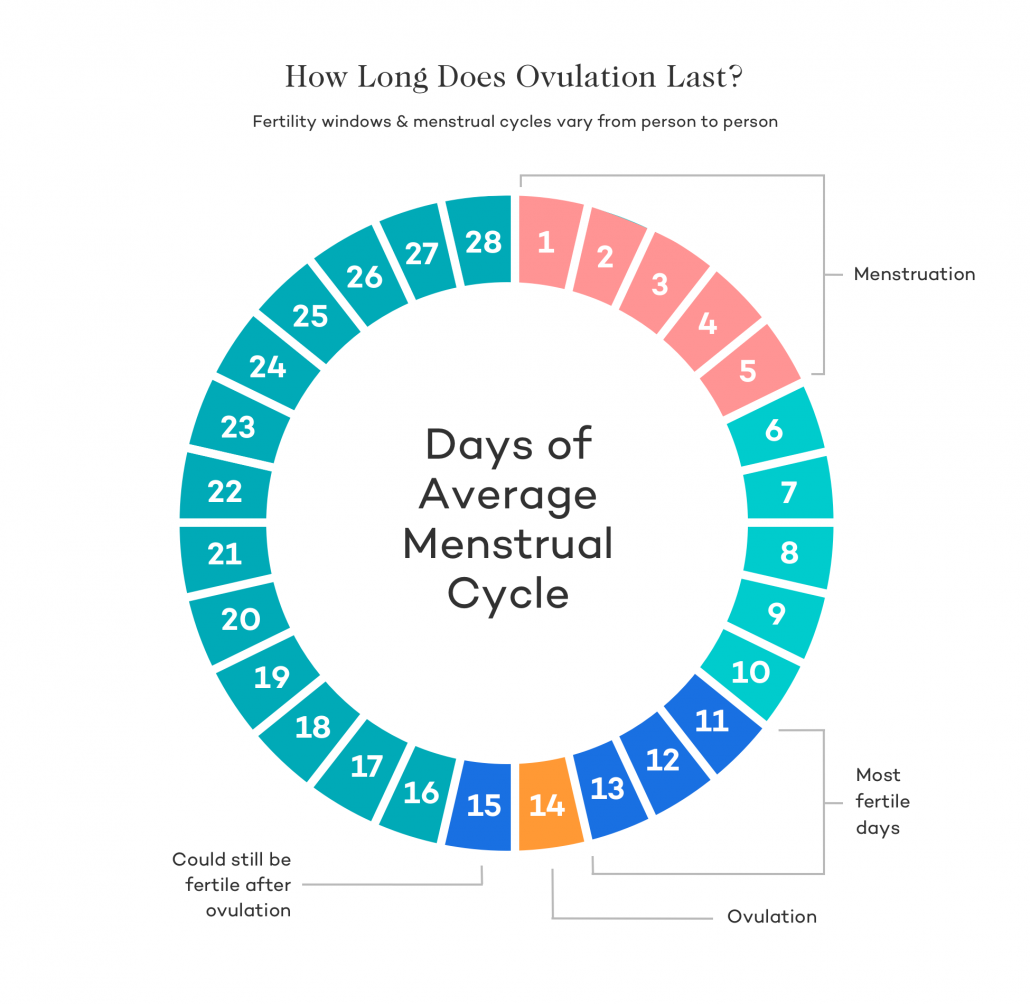
While most fertility specialists say that the fertile window is about five days long, its duration may not be set in stone. Some studies claim a woman’s fertile window can last up to ten days.
Conclusion
Experts recommend having sex during the 72 hours pre-ovulation to fully maximize chances of conception. If sperm arrive before the egg is ovulated, they simply wait in the fallopian tubes until the egg is ready to be released. Studies show that sperm can survive for up to 5 days within a woman’s body.
Pro-fertility Sex Positions
Some experts believe that having sex in the missionary position maximizes your chance of conception.
There’s not much scientific evidence that this is true, however, and much of the available evidence is based on findings from IUI (intrauterine insemination) studies. One IUI study discovered that women who lay flat on their backs for 15 minutes post-insemination have higher conception rates than women who get up immediately.
It’s possible — but not proven — that this concept carries over to actual sex. The chance of conception may improve if a man ejaculates while a woman lays on her back, thus the belief that missionary sex is best for fertility.
Other people speculate that positions that allow for deeper penetration, closer to the cervix, may increase fertility. This belief hasn’t been validated by any research, however. Any sex position that allows sperm to be delivered close to the cervix can result in pregnancy.
Foreplay
Interestingly, foreplay and arousal levels have been shown to positively affect your chances of conception.
Men who are more aroused may have higher sperm counts. And women who orgasm during sex may also be more fertile.
These findings imply that partner attraction is important for fertility — so consider getting in shape with a high-fat, low-carb diet if you haven’t already.
Conclusion
While no sex position has been definitively proven to increase natural fertility, keeping things exciting between you and your partner is always a good idea. Emotional interconnectedness, renewed passion, and reduced stress are all pro-fertility side effects of healthy sex life.
How Often?
Since the sperm’s ability to reach and fertilize an egg is largely a number’s game, couples who have sex more often have higher chances of getting pregnant.
Tracking your period and having sex just prior to ovulation also gives you a higher chance of conceiving. Even if you aren’t tracking your fertility window, having frequent sex increases the chance that sperm will be waiting in the fallopian tubes once an egg is ovulated.
Word of Caution about Lube
Most endocrinologists caution against using lubricants when trying to get pregnant. Most vaginal lubricants are acidic enough to damage sperm and negatively impact fertility. Even in the case of successful conception, it’s not yet fully understood how lube-induced sperm damage might affect future life. Err on the side of caution.
Instead of using lube, we’d recommend focusing on foreplay, which can boost your body’s self-lubrication naturally. The cervical mucus produced by a woman’s body has the ideal thickness and acidity for sperm.
And don’t rush things: a large percentage of women report needing at least 15-20 minutes of kissing and intimacy to really get in the mood.
Conclusion
Lube isn’t likely to increase your natural fertility — and it may harm sperm. Make an effort to focus on increasing arousal instead. Warm water can also be an alternative to potentially toxic lubricants.
Lifestyle Changes for Improved Natural Fertility
Lifestyle changes may seem to be subtle, but they can make a profound difference in your fertility rates over time. Some of our favorite science-backed lifestyle changes include:
- Yoga
- Other exercises
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol
- Get enough sleep
- Avoid toxins
- Avoid saunas
- Reduce stress
- Massage
- Low-level laser therapy
Fertility-friendly Exercise: Yoga
Yoga is a great way to improve your fertility and increase the likelihood of success with fertility treatments. Frequent yoga may improve your natural fertility in three primary ways:
- Reduced stress
- Improved circulation
- Balanced immune system
Let’s take a look at these beneficial mechanisms one by one.
Reduced stress
Stress and fertility problems tend to feed off of each other. Stress can hurt your fertility, and fertility problems, in turn, can cause increased levels of stress.
Yoga is a proven stress-reducer that can help your body produce lower amounts of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
Since cortisol is produced from the same substrate (cholesterol) that pro-fertility hormones like progesterone are, lowering cortisol levels may set the stage for a fertility-friendly environment.
Improved circulation
Poor circulation is a frequent hidden cause of infertility. Conversely, keeping oxygen and carbon dioxide levels high has been correlated with improved fertility because these elements keep the developing fetus healthy.
While ensuring adequate oxygenation can be done by moving to a higher altitude, exercises like yoga are a much more accessible option. Yoga’s gentle movements can increase your blood flow and ensure that nourishing blood reaches your reproductive organs.
Balanced immune system
Yoga is an incredible way to boost your body’s innate immune system. This important facet of the immune system is responsible for managing inflammation.
It’s thought that immunity-induced inflammation is behind many “unexplained infertility” diagnoses, so lowering inflammation naturally is almost always a good idea.
Indeed, yoga’s mental benefits can transfer over to improved physical markers. Studies have shown that yoga practitioners may have higher white blood cell levels.
This shift towards a more ‘rested’ immune state means less stress and higher rates of fertility in those who want to get pregnant.
Yoga’s dual mental and physical benefits may also help couples who are using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) to get pregnant.
Other Fertility-friendly Exercises
The benefits of exercise are as diverse as they are well documented. Exercise is shown to strengthen your heart, improve circulation, reduce stress, improve sleep, and boost fertility.
Experiencing these benefits is as easy as adding 30-60 minutes of moderate movement into your daily routine. The many good choices include walking, swimming, and stretching.
Exercise may boost male fertility, too. Many types of exercise boost testosterone, which in turn plays a vital role in sperm production. Research shows that men who exercise have better testosterone levels and healthier semen.
The Downside of Intense Exercise
While exercise is usually beneficial, it can still be overdone. Fertility specialists like Dr. Kiltz recommend against high-intensity exercise when trying to get pregnant. Intense exercise can easily create more stress than your body can adapt to — and this stress can negatively impact both male and female fertility.
One study from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology shows that exhaustive exercise can reduce a woman’s chances of getting pregnant.
According to their survey of 3,000 women, 24% of women who exercised until exhaustion had fertility problems. Women who exercised at low/moderate intensity showed no evidence of impaired natural fertility. It’s thought that women’s bodies may not have enough energy to support both hard workouts and achieving pregnancy.
If you’ve overdone exercise in the past, however, don’t worry. Reductions in natural fertility seem to fade once hard training is stopped. Supplementing with zinc or B vitamins may also help you regain your fertility.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is known to cause all sorts of health problems, so the fact that it reduces fertility shouldn’t be a surprise. This effect is merely an extension of smoking’s general danger to human health.
It’s believed that the toxins found in cigarette smoke can damage DNA over time — including the DNA of the ovarian follicles where eggs develop. Cigarette smoke can reduce a woman’s ovarian reserve and cause her ovaries to age prematurely, reducing the timeframe in which her body can handle natural pregnancy.
A 2017 study found that smoking more than five cigarettes per day can significantly reduce your fertility. Smoking before pregnancy can also impact your baby’s future health, causing birth defects or even miscarriage.
Fertility experts recommend completely quitting smoking in order to avoid all these potential risks. According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), women who stopped smoking a year before trying to conceive can greatly improve their fertility rates.
Smoking seems to damage male fertility, too. The ASRM notes that smoking can decrease the sperm’s ability to fertilize eggs.
This possibility was confirmed by a 2003 study of over 2,000 men, which found that heavy smokers have 19% less sperm than non-smokers. Sperm density, count, and motility are also affected by smoking. Check out the chart below.
| Sperm Density | Sperm Count | Sperm Motility |
| -15.3% | -17.5% | -16.6% |
Conclusion
All of the available research points to the same conclusion: smoking is bad for every facet of your health, including natural fertility. When trying to quit smoking it can be helpful to look at what you gain, as opposed to what you’re giving up. And when it comes to improving fertility, you could be gaining the child of your dreams.
Limit Alcohol
While having the occasional glass of wine here and there doesn’t seem to impact fertility, excessive alcohol consumption can impair your fertility rates.
Research shows that women who drink 8 or more units of alcohol per week may take longer to conceive than those who abstain.
The effects of moderate alcohol consumption on natural fertility, however, are not as conclusive. In some studies, moderate drinking doesn’t produce any adverse effects — but other studies have correlated as little as five drinks per week with reduced fertility.
While the majority of research in this area has been on women, recent research in males has found that heavy alcohol use has a similarly negative effect.
One study found a distinctive difference in sperm quality between alcoholic and non-alcoholic men. This study also found differences in sperm volume, vitality, and survival rates, and these differences became bigger as more alcohol was consumed.
Only 12% of alcoholics in the study had ‘normal’ healthy semen, while 3 times as many non-alcoholic men had normal semen parameters. The study concluded that alcohol abuse impairs many metrics of sperm health.
Even among people who’ve abused alcohol, however, not all hope is lost. Another study analyzed the semen parameters of chronic alcoholics and found that drastic improvements in semen health could be seen within three months of alcohol withdrawal.
Finally, a review of 15 studies on alcohol and male fertility confirmed that daily alcohol consumption has a negative impact on sperm morphology, volume, and overall health.
Using alcohol and tobacco together may damage sperm even more and lead to sperm DNA damage.
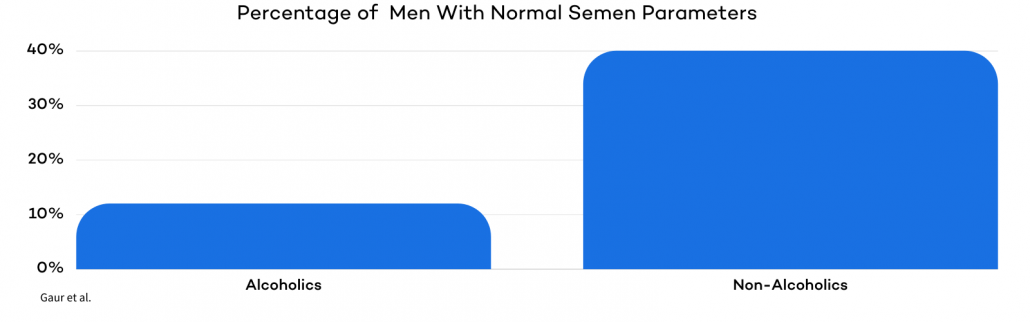
Conclusion
Keeping alcohol consumption a minimum preserves your natural fertility and increases your chances of having a baby.
Get Enough Sleep
Sleep is an often-underlooked facet of health, even among people who truly put a priority on being healthy.
Getting enough sleep is arguably more important than eating well or exercising — at least based on what happens to your body if you don’t sleep.
While couples that struggle with fertility may be tempted to focus solely on their sex life, they would probably do better to focus on a different bedtime activity: sleeping.
Many studies show that inadequate sleep and/or sleep disturbances can hurt the reproductive health of both men and women.
One study of women with sleep issues found that insomnia may increase infertility rates by up to 400%. Given that women are already twice as likely to suffer from insomnia than men, dialing in your sleep routine is of utmost importance.
Sleep can impact every stage of the female fertility process. Poor sleep can negatively impact menstruation, conception, and more. It can even lead to pregnancy complications later on down the road.
Sleeping too much, on the other hand, may also be less than optimal. One study looking at women undergoing IVF treatment found that moderate sleepers (7-8 hours/night) had higher pregnancy rates than both under sleepers (4-6 hours) and oversleepers (9-11 sleepers).
It’s possible this trend was a result of confounding variables, of course. The oversleepers in the study above may have been sleeping more because of some underlying illness or metabolic problem. The best way to make sleep fertility-friendly is simply to listen to your body.
Sleep quality also impacts male fertility. One study of men undergoing fertility treatment found a link between poor sleep quality and lower sperm motility, concentration, and total sperm count.
Another study of 981 healthy men reviewed the effect of sleep patterns on semen health. Just like in the female fertility study mentioned above, this study divided men into three categories: under sleepers, oversleepers, and moderate sleepers. Men who underslept had lower sperm counts, sperm motility, and reduced overall sperm health. Later bedtimes were also correlated with impaired sperm health.
Conclusion
If you want to increase your fertility the natural way, make sleep your priority. We’d recommend a sleep schedule that allows for 7-8+ hours a night.
Try setting yourself up for success by doing some nighttime yoga, meditation, or stretching. Avoiding blue light in the evening may also help you maintain a healthy circadian rhythm.
Avoid Toxins
The phrase “first do no harm” is an underlying tenet of medicine.
It turns out that this concept applies to natural fertility, too. By minimizing your exposure to toxins, you can maximize your body’s natural ability to thrive.
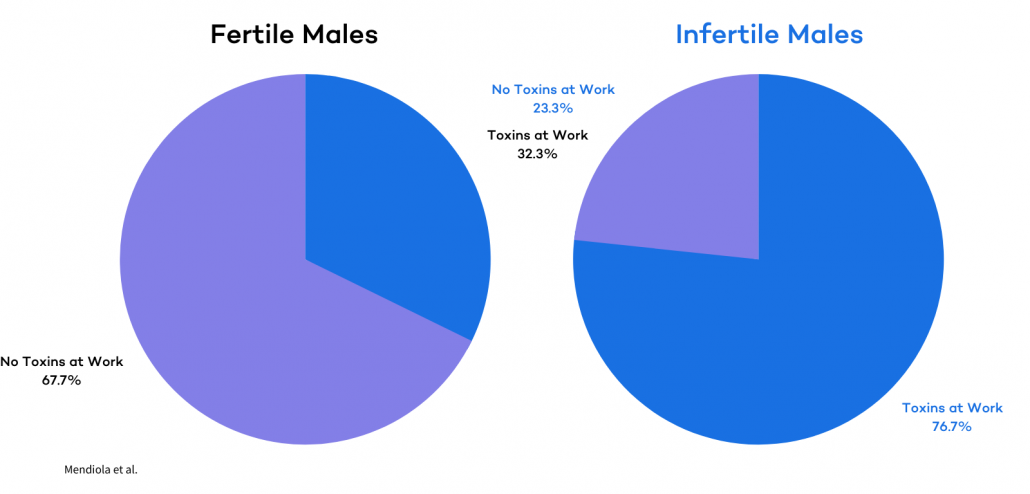
Research has shown that environmental toxins found in the air we breathe, the food we eat, and the beauty aides we use can damage fertility.
These environmental toxins, which include heavy metals, plastic products, and lead, are becoming more unavoidable by the day — causing all sorts of diseases in human populations as they do.
One of the primary aftereffects of exposure to these toxins is reduced fertility. Environmental toxins can disrupt the body’s hormones, and the reproductive systems of both men and women are highly susceptible to this type of disruption. Endocrine impairment can hurt natural fertility and IVF success alike.
One of the most ubiquitous environmental toxins is called bisphenol A, or BPA. This common chemical is found in many types of food packaging, including water bottles, metal cans, and more.
Plastics/metals that contain BPA contaminate the foods and liquids they contain. If you’re pregnant or trying to be, stay away from BPA. One study of women undergoing IVF treatment found that high levels of BPAs significantly impact implantation chances. Women with the top 25% of BPA levels were 211% more likely to suffer from implantation issues.
Do your best to stop using products that contain known toxins. Be conscious of the quality of the foods you consume and try to avoid prepackaged meals. Stay away from non-stick cookware, too.
Avoid Saunas
Sauna use may come with some health benefits, but they’re best avoided by men who are trying to maximize their natural fertility.
The high temperatures of saunas have been shown to cause sperm damage. One study identified a reduction in sperm motility and an increase in sperm defects in men exposed to heat stress.
Another study conducted by the University of California at San Francisco, found that exposure to hot baths/hot tubs can contribute to male infertility. Both dry heat and wet heat (the kind in saunas) may cause impaired spermatogenesis, as reflected in altered sperm parameters and sperm DNA.
If you’ve been exposed to sauna-level heat, don’t panic. Just as with alcohol-induced fertility problems, the effects of heat stress are reversible with time.
Reduce Stress
In general, things that are bad for one’s general health are also bad for their fertility, and stress is no exception.
When our bodies sense stress they recognize it’s not an ideal time to have a baby — and react accordingly. Physical and psychological stress can put your body into a survival mode where fertility is the least of its concerns.
Several recent studies have identified a clear link between a woman’s stress levels and her fertility. One study found that women with high stress levels took 29% longer to get pregnant than women with more ‘normal’ stress levels.
The relationship between stress and fertility is especially complex because both things affect each other. In other words, stress can be both a cause and an effect of infertility. Stress tends to increase after a diagnosis of infertility or failed IVF treatment.
Stress can affect male fertility, too. Studies show it can reduce the production of luteinizing hormone and testosterone. These changes complicate the process of spermatogenesis and result in reduced sperm quality.
Thankfully, stress may have a simple solution. One review of more than 30 studies found that relaxation techniques may be effective at reducing negative emotions in medical patients. Psychosocial interventions that focus on eliminating stress can also help to improve pregnancy rates for infertile couples.
Massage
Massage therapy offers both physical and mental benefits. It improves circulation, reduces muscular tension, reduces stress, and helps you relax.
Since stress can negatively impact fertility, massage therapy may offer a holistic method for increasing fertility rates.
Fertility-specific massage targets the muscles and connective tissues that surround the reproductive organs and gently corrects blockages. This results in increased blood flow, which helps your body regenerate and regulate itself.
Many couples who try fertility massage experience improved fertility rates, especially when massage is used in conjunction with a fertility diet and other tools like meditation.
While more research is needed in this area, the existing data suggests that massage can help treat several known causes of infertility. One study of 1,392 women found that massage helped unblock the fallopian tubes of 60% of its participants. Over 50% of these women were then able to achieve natural pregnancy. A special type of massage therapy may also help with male fertility.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is another great way to relieve stress. This ancient practice uses sterilized needles to stimulate your body’s energy pathways and improve circulation. Research shows that acupuncture makes your brain release endorphins and endocannabinoids, natural painkillers that can help reduce stress.
Acupuncture is also known to have a fertility-friendly, hormone-balancing effect. It may help reduce the depression that’s all too common in people undergoing infertility treatment.
These benefits are reflected in real-world research: women undergoing IVF have increased birth rates if they undergo acupuncture treatment throughout the fertilization process.
Low-level Laser Therapy
Different types of light transmit different types of information to the creatures that absorb it. While blue light can be toxic to human cells, red light is energizing.
Recent studies have begun to establish a connection between natural fertility and low-level laser therapy (LLLT). This type of therapy has traditionally been used to relieve pain or enhance cellular function, and may also stimulate blood flow to the reproductive organs enough to improve fertility.
One Japanese study of infertile women who had previously unsuccessful results with assisted reproductive treatments discovered just how effective LLLT could be. This study started off with an initial trial of 74 patients, 16 of whom achieved pregnancy.
Due to the initial success this trial was expanded to include 701 patients, 156 of whom went on to achieve pregnancy. In both cases, over 20% of the women who tried LLLT were able to become pregnant. No adverse events were noted in any of the patients who benefited from LLLT.
Study researchers concluded that laser therapy is a pain-free, low-risk way to assist women during fertility treatment. Laser therapy may be especially helpful for older women who experience an age-related decline in egg quality.
LLLT may enhance natural fertility for males, too. Studies show it can increase one’s percentage of living sperm cells and improve their motility. Compared to other male infertility treatments, LLT is remarkably free from side effects. Many leading researchers believe it should be used as widely as possible.
Optimizing Nutrition for Natural Fertility
The importance of nutrition is right up there with lifestyle when it comes to maximizing natural fertility.
The ideal fertility diet, however, may look a little different than you might expect — especially if you’re not familiar with Dr. Kiltz’s B.E.B.B.I approach. Here’s what you need to know about eating for reproductive health.
Dietary Tip#1: Eat High Fat
Inflammation is one of the primary root causes of infertility. While transient ebbs and flows in inflammation may be helpful for wound healing, immune responses, et cetera, chronic inflammation is harmful enough to hurt your fertility rates.
An overactive immune system can damage sperm, egg, embryo, and the developing fetus. Inflammation can make it difficult to get pregnant and stay pregnant.
Dr. Kiltz’s natural fertility diet makes reducing inflammation a primary goal. Since your body burns fat more ‘cleanly’ than it burns carbs, getting most of your calories from fat may set the stage for an anti-inflammatory, pro-fertility internal environment.
Fat fosters fertility in other ways, too. It provides building blocks for the membranes of your cells and helps your thyroid synthesize important reproductive hormones.
Dietary fat also provides your body with essential fatty acids that it can’t produce on its own. The fatty acids found in animal products assist with blood clotting and increase overall brain function.
Dietary fat also allows your body to absorb some of the most important fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin K. All of these vitamins play a role in supporting fertility.
Dietary Tip #2: Eat Animal Products
Natural fats from high-fat animal products are also a natural fertility ally. These fats keep the lymphatic system firing on all cylinders, literally ‘lubricating’ it with fatty acids. Dr. Kilt’z B.E.B.B.I diet recommends the following animal-derived products:
- Bacon (in the form of fresh pork belly)
- Eggs
- Butter
- Beef
- Ice Cream (Dr. Kiltz’s keto homemade)
Besides being a rich source of cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins, these foods also contain many other fertility boosting nutrients.
Full-fat dairy contains complete protein and known fertility-friendly nutrients, including calcium, zinc, choline, selenium, spermidine, and more.
In addition to supporting bone, heart, and connective tissue health, calcium is directly involved in sperm production in men. Be sure to get your calcium from full-fat dairy sources — studies have shown that reduced-fat dairy isn’t as healthy.
Dietary Tip #3: Avoid Trans Fats
Just as important as the inclusion of health-promoting foods is the exclusion of toxic ones. Trans fats are among the most toxic food ingredients.
Highly processed foods are the most common source of trans fats. These types of fats are very unstable and high in inflammatory omega-6 fatty acids. Research has shown that they’re associated with ovulation problems and infertility.
One eight-year-long observational study found that eating a diet high in trans fats resulted in reduced fertility. Trans fats have also been linked to male infertility.
Artificial trans fats can be found in fast food, snack foods, baked goods, and other processed foods. These processed foods usually contain partially hydrogenated oils, which may be the worst type of trans fats. We recommend checking for partially or fully hydrogenated oils on the ingredients list of any food you buy.
Dietary Tip #4: Reduce Carbohydrate Intake
While an excess of fat has traditionally been blamed for causing obesity, new research shows that excess carbohydrates trap fat in fat cells by triggering insulin production. The Standard American diet is rich in carbohydrates and unhealthy fats that directly contribute to inflammation, insulin resistance, weight gain, and infertility.
Chronically high carb intake can also cause elevated blood sugar levels, which leads to the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGE’s) and other types of structural damage.
Grains are especially inflammatory since they contain the perfect blend of sugar and inflammatory plant proteins like gluten. Given that the carbohydrates and incomplete proteins found in grains aren’t an essential part of the human diet, you’re probably better off going without them.
Chronically high carb consumption can also affect reproductive hormone levels. Spiking insulin levels may throw off your reproductive hormone levels enough to cause anovulation or other fertility problems.
Common foods that are high in sugar and carbs include:
- bread
- pastries
- rice
- potatoes
- fruit
- candy
Dietary Tip #5: Limit Caffeine
Coffee is a seemingly essential part of many people’s mornings. Thankfully, you don’t have to give up coffee cold turkey in order to maximize your fertility. Enjoying a cup of coffee each morning is fine.
Having multiple cups of coffee or other caffeinated drinks each day, however, can negatively affect your fertility. It’s a good idea to closely monitor your caffeine intake if you’re trying to conceive.
Dietary Tip #6: Cut Fiber
Fiber is the portion of plant-based foods that your body can’t fully break down. Fiber may keep the digestive system healthy by encouraging regular bowel movements. In theory, at least.
Newer research shows that eating too much fiber could negatively impact female fertility.
One case study that followed 250 women for two years discovered that high fiber intake was associated with lower reproductive hormone levels. More specifically, women who ate large amounts of fiber had lower levels of estradiol, progesterone, LH, and FSH.
Study researchers concluded that the hormonal changes caused by a high-fiber diet are associated with a higher probability of anovulation in women.
Dietary Tip #7: Limit Soy
Soy products today aren’t what they once were. While soy is a staple in most traditional Asian diets, today’s soy isn’t properly prepared — which means it contains extremely high levels of phytoestrogens and antinutrients.
Phytoestrogens are especially damaging to male fertility, since men’s bodies are designed to be high in testosterone and low in estrogen. One study involving 99 men showed that a higher soy intake is associated with lower sperm concentration.
Soy isn’t optimal for women, either. Eating excess soy can lead to lower circulating levels of hormones, like gonadotropin, that are essential for a healthy female reproductive cycle. Moderation is key when it comes to soy ingestion: diets containing small amounts of soy don’t seem to pose a threat to the function of the ovaries.
Dietary Tip #8: Consider supplementing
As a general rule, eating whole foods and animal-based superfoods is almost always better than resorting to supplements.
The higher nutrient demands of pregnant women, however, mean that getting all your vitamins and minerals through food alone can be impractical. B vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin K2 can be especially difficult to get via diet.
Many women find that natural fertility supplements provide an excellent way to safeguard both their health and the health of their future babies. Our team of fertility specialists recommends specialized supplements to all couples who are having difficulty conceiving.

The Molecular Fertility supplements we recommend are designed by leading fertility experts and backed by the latest peer-reviewed science. Rich in time-tested, clinically-proven nutrients, thousands of men and women are using our supplements to maximize their fertility the natural way.
Dietary Tip #9: Get Enough Iron
Iron is another nutrient that’s needed more than normal during conception and pregnancy.
An essential mineral our bodies need for growth, development, and hormone production, iron is naturally found in meat, seafood, beans, and lentils. The heme iron found in animal products is more bioavailable than plant-derived options.
Iron is also needed to make hemoglobin and myoglobin, the components of red blood cells that oxygenate muscles, organs, and tissues. Since the amount of blood in a woman’s body increases by up to 50% during pregnancy, extra iron is needed to maintain circulatory health.
Low iron levels can lead to a lack of ovulation and increase a woman’s risk of infertility.
Dr. Kiltz and other fertility specialists recommended taking iron supplements during conception and throughout pregnancy for this very reason. Supplementing with iron has been shown to greatly reduce the risk of ovulatory infertility. In addition to helping with ovulation, taking iron supplements prior to conception can ensure that you don’t become anemic during pregnancy.
Dietary Tip #10: Antioxidants
Antioxidants are found in many fruits, vegetables, and animal-based superfoods. Many health professionals believe that antioxidants are a critical part of any healthy diet.
Antioxidants are able to defend our cells from the oxidative damage that happens when normal metabolic processes generate unstable free radicals. Antioxidants essentially prevent our bodies from getting oxidized (think of rust on metal). Common antioxidants include vitamin C, vitamin E, astaxanthin, and glutathione.
Studies show that antioxidants like folate and zinc may improve fertility in both men and women. The antioxidants in walnuts, for example, can tangibly improve sperm quality.
Antioxidants may also make IVF treatments more effective — one study showed a 23% increase in fertility rates when IVF and antioxidant supplements were used in conjunction.
Dietary Tip #11: Vitamin D
If you’re trying to increase your natural fertility, be sure to get enough vitamin D. Adequate Vitamin D intake boosts fertility by helping your body produce critical steroid hormones. Vitamin D deficiency, on the other hand, has been linked to infertility in both sexes.
Men may experience reduced sperm health if their vitamin D levels are low, while women may need to supplement with vitamin D to ensure healthy levels throughout pregnancy.
One study found that women with adequate vitamin D levels had an 18% higher chance of pregnancy during IVF treatment than women with low levels. The importance of vitamin D grows even more apparent given that almost 40% of U.S. adults suffer from Vitamin D deficiency.
Since vitamin D comes from the foods we eat and from the sun, getting enough of this vitamin requires a multifaceted approach.
Sunlight is the single best source of vitamin D. The moment our skin gets exposed to sunlight, a chemical reaction occurs and vitamin D gets produced. At the right latitudes, Just 10-15 minutes of exposure to strong sunlight per day may be enough to ensure adequate vitamin D production.
Vitamin D can also be obtained through food. This source becomes especially important in higher latitudes and during periods of cloudiness and wintertime. Foods high in vitamin D include seafood, salmon roe, beef, eggs, and mushrooms grown under UV lights.
Get Tested (STDs and STIs)
STDs (sexually transmitted diseases) and STIs (sexually transmitted infections) are known to negatively impact fertility in both males and females. Strongly consider getting tested if there is any possibility that either you or your partner have an STD/STI.
In women, STDs can lower fertility and increase the chances of experiencing a miscarriage. In men STDs can cause inflammation of the testicles and reduce semen quality.
Getting tested is important — these diseases are more common than you might think. According to the World Health Organization, there were 273 million cases of curable STIs in adults aged 15-49 in 2012 alone.
PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome)
Polycystic ovarian syndrome is the number 1 most common cause of infertility in women. Many women unknowingly suffer from PCOS for years before learning they have it when they first try to get pregnant.
Women with PCOS have enlarged ovaries that develop small cysts. These cysts, while not malignant or cancerous, can cause hormonal imbalances that disrupt healthy ovulation. Studies have shown that improper ovulation is the cause of up to 30% of infertility cases.
If you suspect you have PCOS, see your doctor. Eating a keto diet may also help correct the root causes of this reversible disease.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a uterine disorder where tissues that normally grow within the uterus grow on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or intestines instead.
Endometriosis is known to reduce fertility in several ways, largely by impairing normal egg fertilization and transport.
Click here to learn more about endometriosis and how to correct it.
Natural Fertility: The Outlook
So, there you have it! Wrestling with infertility may seem like a hapless cause — but the reality is that natural dietary and lifestyle changes can lead to profound improvements over time.
Fostering an intimate sex life, reducing environmental toxins, living a lower-stress life, eating a nourishing diet, and taking safe fertility supplements are all viable ways to maximize your natural fertility.
And remember to be patient, since both sperm and egg take between 75 and 90 days to fully develop.