We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Vitamin D and COVID 19: What you need to Know

Table of Contents
There are many fascinating correlations between COVID-19 and vitamin D deficiency. And addressing vitamin D deficiencies has important health implications far beyond the COVID-19 pandemic.
Key Points:
- Vitamin D supports the immune system.
- 80-90% of people are Vitamin D deficient
- Vitamin D deficiency has been correlated with a higher risk of infection from COVID-19.
How the Link Between Vitamin D and COVID 19 was Discovered
The link between Vitamin D and reductions in COVID-19 infection rates first came to light in an unlikely population; the homeless.
In the early days of the pandemic Dr. Jim O’Connell, President of the Boston Healthcare for the Homeless Program, recognized that something very strange was taking place in the people he treated.
Despite limited access to hygiene and the impossibility of social distancing at crowded shelters, Dr. O’Connell was perplexed to find almost no symptoms of COVID showing up in this vulnerable population.
By late March 2020, as national cases reached over 80,000, Dr. O’Connell still wasn’t seeing anywhere near the number of cases he expected. His colleagues in Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle, and Atlanta, were all making the same counterintuitive observations.
This was in early 2020 before testing was widely available. To get tested a person had to be symptomatic. When the first cases finally appeared in the Boston shelters, Dr. O’Connell began testing anyone who had been in contact with the confirmed cases. That’s when things got even more surprising.
Of the 408 people Dr. O’Connell tested at one of Boston’s largest shelters, 147 people, or nearly 40% came back positive for COVID-19. Yet almost all of these carriers were asymptomatic, meaning they showed no signs of having contracted the virus.
Data from other homeless facilities told the same story. A sky-high positive test rate of 30-40%, yet a near complete absence of symptoms among COVID-19 carriers.
Dr. O’Connell and colleagues were stumped. How could it be that this vulnerable population with high rates of positive tests weren’t getting ravaged by the kinds of symptoms killing tens of thousands of Americans and sending millions more to the ER?
One hypothesis put forward by Dr. O’Connell was that the homeless population spends more time outside. More time outside means more sun, giving them consistent exposure to the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D.
This raises the question: How might vitamin-D affect COVID-19?
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that naturally occurs in some foods, such as certain mushrooms (especially mushrooms grown under UV lights), egg yolks, and a variety of different kinds of fatty fish, and fish products, including salmon, herring, sardines, and tuna. Vitamin D can also be taken as a dietary supplement. Your body produces Vitamin D on its own when sunlight strikes your skin triggering vitamin D synthesis.
Vitamin D is essential to important functions in your body including absorption of calcium and phosphorus and supporting the function of your immune system. A sufficient amount of vitamin D is critical for the growth of bones and teeth, as well as improved resistance against viruses and disease.
Common foods that contain vitamin D include:
| Food Type | MCG Per Serving | % Daily Value |
| Cod liver oil, 1 tablespoon | 34.0 | 170 |
| Trout (rainbow), farmed, cooked, 3 ounces | 16.2 | 81 |
| Salmon (sockeye), cooked, 3 ounces | 14.2 | 71 |
| Mushrooms, white, raw, sliced, exposed to UV light, ½ cup | 9.2 | 46 |
| Whole milk (fortified) | 2.9 | 15 |
| Beef liver 3 oz. | 1 | 5 |
Dr. Fauci on Vitamin D and COVID-19
Dr, Anthony Fauci, the Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, and a key member of the US Government’s COVID-19 task force, stated in an interview, “If you are deficient in vitamin D, that does have an impact on your susceptibility to infection…So I would not mind recommending — and I do it myself — taking vitamin D supplements.”
Dr. Fauci’s recommendation is based on the acknowledgment that vitamin D supports the immune system. A healthy immune system is our first line of defense against viruses.
Due to the observations of frontline doctors like Jim O’Connel and others, a number of studies have been launched to better understand the role that vitamin D plays in protecting against COVID 19. The preliminary evidence is compelling.
The Science of Vitamin D and COVID-19
There are now numerous observational studies and broad reviews of current evidence demonstrating that low vitamin D levels are associated with higher risks of getting COVID-19, and with more serious and life-threatening symptoms.
According to Dr. Shad Marvasti, professor of preventive medicine at the University of Arizona, low vitamin D levels are associated with an increase in cytokines. Cytokines are cell-to-cell chemical messengers responsible for inflammation. This also leads to lower levels of protective immune cells.
Other associations between low vitamin D and COVID-19 have been made in terms of where people live with regards to sunshine.
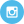
A recent study shows a correlation between mortality from COVID-19 and countries north of 35 degrees north latitude, in the Northern Hemisphere, or 35 degrees south in the Southern Hemisphere.
Populations in countries between the 35-degree latitude lines are able to get enough sun in the winter to produce adequate vitamin D. Whereas populations outside the 35-degree latitude lines (further from the equator) cannot get enough sun during the winter to produce sufficient vitamin-D.
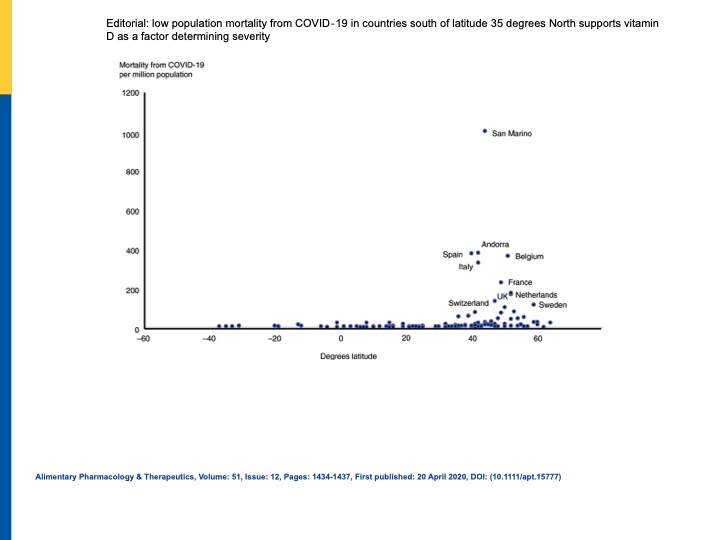
A study looking at vitamin D deficiency and mortality rates from COVID-19 showed that the higher the vitamin D level in the population of a country, the lower the COVID-19 cases.
Other studies looking at potential connections between vitamin D and COVID-19 demonstrated that sufficient levels of vitamin D before infection appear to make people less likely to have severe complications from COVID-19.
Inversely, there appears to be a connection between vitamin D deficiency prior to infection and those who experience strong adverse reactions to COVID-19.
These studies looking specifically at the role of vitamin D for preventing or reducing the severity of vitamin D, reflect numerous earlier studies revealing the role of vitamin D as an antiviral against common viruses like the flu.
Vitamin D and Immunity
A study of 334 school children demonstrated that those taking vitamin D supplements were nearly half as likely to contract the flu virus.
A review of 25 high-quality randomized control trials identified a strong role for vitamin D supplementation in the prevention of acute respiratory tract infections. This review found that adequate vitamin D can reduce the risk of respiratory infection by up to 70%.
In addition to boosting our immune systems against external invaders, vitamin D is shown to be vital for the body’s autoimmune function. Studies reveal that vitamin D helps the body reduce harmful inflammatory responses that lead to numerous diseases and disorders including heart disease and diabetes.
Key takeaways
Getting enough vitamin D in our diet and from safe sun exposure is a critical component of a healthy immune system.
While more research is necessary to fully understand the links between vitamin D, vitamin D deficiencies, and COVID-19, preliminary studies show that getting enough vitamin D may reduce your likelihood of contracting COVID-19, and is likely supportive against adverse reactions to COVID-19.
A diet low in sugars and high in fatty animal products can help you get and absorb the vitamin D we need to stay healthy.