We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
What to Eat During Intermittent Fasting: Meal Plan and Food List
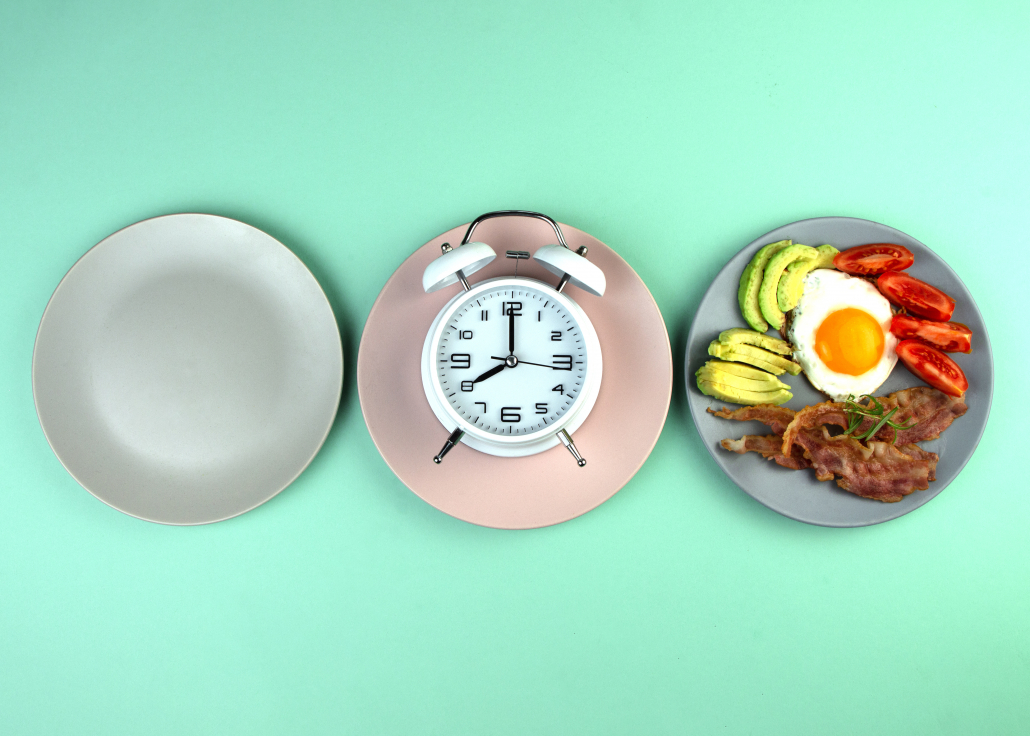

Intermittent fasting offers many benefits. But meal timing alone isn’t enough to ensure IF success. Knowing what foods to eat while intermittent fasting is as important as knowing when to eat them. This intermittent fasting food list will help you chose what to eat during intermittent fasting.
Sticking with the best foods to eat while fasting can increase the science-backed benefits of IF including reduced inflammation, boosted metabolism, improved cognitive function. [1]
In this article, we’ll explore the foods to eat while fasting and the research behind our recommendations.
Table of Contents
Why Food Matters When Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting activates a process called autophagy where your immune system destroys old, damaged cells, then recycles their individual components into new, healthy cells. [2] Think of it as cellular spring cleaning.
Feeding these new forming cells with optimal energy sources is critical.
Healthy fats and complete proteins found in superfoods sourced from animals are the best foods to break an intermittent fast.
Failure to nourish your regenerating cells with whole animal foods can promote metabolic dysfunction and increase your risk of developing certain types of cancer. [3]
What to Eat During Intermittent Fasting
When eating during intermittent fasting it is crucial to avoid foods that damage your cells.
Unfortunately, most foods on the Standard American Diet are processed, and loaded with added sugar and vegetable oils, making them highly inflammatory.
Here’s a list of foods to avoid while practicing IF:
- Processed grains
- Gluten
- High-carb fruits
- Processed foods
- Added sugars
- Industrial vegetable oils
Intermittent Fasting Food List
Avoiding the above foods and food groups isn’t nearly as limiting as you might think. check The following intermittent-fasting-friendly options provide a variety of nutrient-rich options.
Foods to Eat While Intermittent Fasting
- Red meat (grass-fed and pasture raised when possible)
- organ meats
- Eggs
- Butter
- Tallow
- Low-carb yogurt
- Bone broth
- Oysters, Salmon roe fatty fish, and other seafood
- Low-carb fruit like berries
- Properly-prepared low-carb vegetables
- Low-toxin veggies like sweet potatoes
It is no surprise that these healthy whole foods have been the cornerstone of traditional cuisines for millenia.
Thanks to pioneering researchers like Weston A. Price, we know that peoples who practiced nose-to-tail eating lived longer and had extremely low incidences of the chronic inflammatory diseases that kill most people today like heart disease and cancer. 4
These are also the foods featured in modern ketogenic and carnivore diets.
It is worth noting that combining intermittent fasting and keto have been shown to mutually increase the benefits of each dietary approach.
Now let’s take a closer look at the nutrition and benefits of specific foods to eat while fasting.
Healthy Fats
Intermittent fasting causes your body to reduce its reliance on carbohydrates and switch into fat-burning mode.
Maintaining the benefits of fat-burning throughout your daily eating window is simple: Focus on high-fat, low-carb whole foods.
For many people a high-fat recommendation will raise some eyebrows. But contrary to popular belief, whole-food saturated fats are not responsible for heart disease.
A landmark 2020 paper published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, found that “whole-fat dairy, unprocessed meat, eggs, and dark chocolate are SFA-rich foods […] that are not associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The totality of available evidence does not support further limiting the intake of such foods.” [4]
On the contrary, recent research shows that some saturated fats are in fact great for human health. [5] The stearic acid contained in beef and dark chocolate, for example, activates the energy-producing mitochondria within your cells en route to boosting your metabolism and fostering weight loss. [6]
While olive oil, butter, ghee, and many other fats are all great choices, two of our favorite IF-friendly fats are tallow and coconut oil.
Tallow
Tallow is a type of animal fat (most often from beef) that’s been cooked down into a shelf-stable form. [4]
Tallow is rich in fat-soluble vitamins and other nutrients. Grass-fed tallow’s nutritional profile is even better — it’s higher in vitamin E and omega 3’s. [7]
| Macronutrient | Per tablespoon | Per 100 grams |
| Calories | 115 calories | 902 calories |
| Carbohydrates | 0 grams | 0 grams |
| Total Fat | 13 grams | 100 grams |
| Saturated | 6.4 grams (59%) | 49.8 grams |
| Monounsaturated | 5.4 grams (42%) | 41.8 grams |
| Polyunsaturated | 0.5 grams (4%) | 4 grams |
| Omega 3 | 0.08 grams (0.6%) | 0.6 gram |
| Omega 6 | 0.4 grams (3.1%) | 3.1 grams |
| Protein | 0 grams | 0 grams |
Tallow’s unique blend of nutrients and fatty acids makes it among the most pro-metabolic foods.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is one of the most saturated whole-food fat sources. It’s rich in medium-chain triglycerides, a special type of fat that gets metabolized in the liver as if they were carbohydrates.
The MCT content of coconut oil makes it a great compliment to intermittent fasting. Consuming coconut oil during your eating window can keep your ketone levels elevated.[8]
Some people find that a coconut oil-rich diet allows them to eat 100+ grams of carbs a day and remain in ketosis. [9]
One word of caution about coconut oil: it can have a laxative effect if you’re not used to it. Start off with consuming just a teaspoon or two a day, then add more over time.
Ruminant Meats
The meat from ruminant animals (beef, lamb, bison, etc) is a crucial addition to any intermittent fasting food list. These meats are extremely satiating and packed with important unique nutrients.
Unlike the nutrients found in most plant products, ruminants have done the work for us and converted their nutrient contents into the most bioavailable forms. Ruminants have four-part stomachs that are perfectly suited to digesting plants — it makes more sense to let them eat plants and then eat them. [17]
Ruminants can even convert any PUFA (polyunsaturated fats) present in their feed into healthier saturated fats. [18]
Ruminant meats are generally rich in vital B vitamins, zinc, heme iron, stearic acid, and more. Below are the nutrient stats for beef rib eye:
| Nutrient | 225g Rib Eye | Recommended Daily Value (RDV) | % RDV |
| Calories | 655 cal | 2500 | 18.6% |
| Protein | 54g | 60g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 90% |
| Fat | 50g | 30g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 166% |
| Saturated Fat | 23g | 20g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 115% |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 25g | ||
| Carbohydrates | 0g | 1200g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 0% |
| Niacin (B-3) | 13.5mg | 16mg | 30% |
| B 6 | 1.4mg | 2mg | 70% |
| Selenium | 56.25 mcg | 67mcg | 84% |
| Iron | 3.24mg | 20mg | 16% |
| Magnesium | 144mg | 420mg | 34% |
| Zinc | 9.45mg | 11mg | 86% |
| Potassium | 666mg | 4000mg | 17% |
| Phosphorus | 400mg | 700mg | 57% |
Perhaps it’s telling that even the godfather of 16/8 intermittent fasting himself, bodybuilder Martin Berkah, advocated for high ruminant meat consumption during the eating window. Don’t skimp on the meat if you want to experience similarly great results from your own IF plan. [19]
Organ Meats
For most people organ meats are taboo, or exotic at best.
Yet, organ meats account for many of the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet. So it’s no surprise that when we look at the role of diet in human evolution, we see that organ meats were the most important fuel source for humans for most of our existence.
We also see that during most of human history, our species ate far less frequently. In fact, it’s likely that intermittent fasting was the norm. When our ancestors enjoyed a successful hunt they feasted. In between hunts they fasted.
So, from an evolutionary perspective organ meats are likely the best foods to eat during intermittent fasting.
Different organ meats have different nutrient profiles, but selecting the right organ meat can be quite simple. Based on the like-supports-like concept, eating any particular organ meat may strengthen the corresponding organ(s) of your body. [10]
Let’s take a look at some of the most popular and accessible organ meats.
Liver
Beef liver is a natural multivitamin. It’s so high in certain nutrients, in fact, that it shouldn’t be eaten too often. View liver as more of a supplemental food. [11]
If you don’t enjoy the taste or smell of liver you can still get its benefits from quality, grass-fed Beef Liver Supplements.
Sweetbreads
Sweetbreads are neither sweet nor bready, but what they lack in etymological sense they make up for in nutrition. The term sweetbread can refer to any of several beef organs, including the thymus and pancreas. [12]
Can’t find sweetbreads at your local health food store or farmer’s market? Not a problem. They can also be consumed in quality Organ Meat Supplements.
Kidney
Beef kidney is rich in unique peptides, antioxidants, and blood-boosting factors that may directly improve your own kidney health. [13]
Most people don’t exactly enjoy the taste of beef kidney, but like the other organs on the list you can get them in freeze-dried tablets.
Brain
Though not as common in American diets, brain as food is a staple around the world.
Beef brain is nature’s very best source of cholesterol — even better than egg yolks. [14]
Fittingly, this cholesterol serves as the precursor to brain-boosting hormones (pregnenolone, progesterone, DHEA, and more). [15] Beef brain provides an excellent fuel source for our own energy-hogging human brains. [16]
Unfortunately, sourcing and buying high-quality brain can be a challenge. That’s where Dr. Kitlz’s Nutritional Solutions Organ Meat Supplement comes in. It’s one of the few on the market that features beef brain alongside more common beef organs.
Full-Fat Dairy
High in quality fats and proteins, while low in carbs, full-fat dairy can be a fantastic addition to your intermittent fasting food list. .
Nutritional analysis has found that butterfat is comprised of more than 400 beneficial fatty acids. [20] One such acid is butyric acid, which has been shown effective in blocking the growth of colorectal cancer, and to reduce symptoms of Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome. 1 2
One common full-fat dairy product is Parmigiano Reggiano, an aged cheese that’s still made according to old-world standards:
| Nutrient | 100g of Parma | Recommended Daily Value (RDV) | % RDV |
| Calories | 420 calories | 2,500 calories | 17% |
| Protein | 32 grams | 50 g (standard diet, not keto) | 64% |
| Fat | 30 grams | 30 g (standard diet, not keto) | 100% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.4 grams | 120 g (standard diet, not keto) | 2.8% |
| Niacin | .3 milligrams | 16 mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 24 micrograms | 70 mcg | 34% |
| Iron | 0.9 milligrams | 20 mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 47 milligrams | 420 mg | 11% |
| Zinc | 2.9 milligram | 11 mg | 37% |
| Potassium | 221 milligrams | 4000 mg | 4.7% |
| Phosphorus | 737 milligrams | 700 mg | 105% |
Other great dairy products include:
- Butter or ghee
- Aged/smoked cheeses
- Unsweetened yogurt
- Creme fraiche
- Sour cream
Fish and Seafood
Fish makes a great addition to your intermittent fasting meal plan. It’s keto and carnivore friendly, and it provides many of the benefits of ruminant meat.
Fish is also lower in iron than red meat. This can be beneficial because iron — while a truly vital nutrient — is surprisingly easy to overdo. [21]
Below is the impressive nutrient profile of salmon roe, considered the most nutritious part of the fish:
| Nutrient | 100g of Salmon Roe | Recommended Daily Value (RDV) | % RDV |
| Calories | 250 calories | 2,500 calories | 10% |
| Protein | 29 grams | 50 g (standard diet, not keto) | 58% |
| Fat | 14 grams | 30 g (standard diet, not keto) | 47% |
| Carbohydrates | 2.9 grams | 120 g (standard diet, not keto) | 2.4% |
| Niacin | 1.8 milligrams | 16 mg | 20% |
| Selenium | 40 micrograms | 70 mcg | 73% |
| Iron | 0.6 milligrams | 20 mg | 3.3% |
| Magnesium | 20 milligrams | 420 mg | 4.8% |
| Zinc | 1 milligram | 11 mg | 9% |
| Potassium | 221 milligrams | 4000 mg | 4.7% |
| Phosphorus | 402 milligrams | 700 mg | 57% |
And if salmon roe proves too hard to find, eating the salmon itself–especially the fattiest kind called King Salmon–is a close second in terms of nutrition.
| King Salmon (Wild) | Amount per 4 oz. | % RDA |
| Fat | 12g | |
| Saturated Fat | 2g | |
| Cholesterol | 61mg | |
| Protein | 20g | |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin B12 | 7.4µg | 308% |
| B3 | 8.4mg | 53% |
| B6 | .3mg | 21% |
| B5 | 1gm | 21% |
| Vitamin A | 453.0IU | 15% |
| B1 | .2mg | 13% |
| B2 | .2mg | 13% |
| Vitamin E | 1.5mg | 10% |
| Minerals | ||
| Selenium | 31.0µg | 56% |
| Phosphorus | 208.0mg | 21% |
| Potassium | 370.0mg | 10% |
| Magnesium | 24.0mg | 6% |
Oysters make another great seafood addition to an intermittent fasting food list. They’re loaded with nutrients.
A 3.5 ounce serving contributes only 68 calories while providing more than 100% of your RDV for vitamins B12, zinc, and copper — and over 75% of your RDV for vitamin D and selenium. [2]
| RAW OYSTER CALORIES | 68 CALORIES | % RDV |
| PROTEIN | 7 grams | 8% |
| FAT | 2.5 grams | 1% |
| CARBS | 3.9 grams | 4% |
| VITAMIN A | 100 IU | 2% |
| VITAMIN D | 320 IU | 80% |
| VITAMIN E | 1 mg | 4% |
| VITAMIN K | 0 mcg | 0% |
| VITAMIN B1 | 0.1 mg | 7% |
| VITAMIN B3 | 1.4 mg | 7% |
| VITAMIN B12 | 19.5 mcg | 324% |
| IRON | 6.7 mg | 37% |
| MAGNESIUM | 47 mg | 12% |
| PHOSPHORUS | 135 mg | 14% |
| ZINC | 90.8 mg | 605% |
| COPPER | 4.5 mg | 223% |
| MANGANESE | 0.4 mg | 18% |
| SELENIUM | 63.7 mcg | 91% |
Low Toxicity Vegetables
Not all vegetables are created equal. Surprisingly, not all veggies are even good for you. The best veggies on your intermittent fasting food list are low in both carbs and plant toxins and antinutrients.
It’s worth noting that some veggies like broccoli contain compounds like sulforaphane that have been studied for their beneficial and anti-cancer properties. But these same compounds can also cause cellular damage. 2
Consider that these are naturally occurring pesticides meant to kill predators. In our bodies they can act like chemotherapy, a benefit in targeted doses. But subjecting yourself to chronic low-dose chemotherapy is not a good idea.
When considering what these chemicals are and how they affect our cells explains why there are no reliable studies confirming a net positive for eating vegetables.
That said, consuming the following veggies in moderation and when prepared properly is likely fine.
- Asparagus
- Avocado (technically fruit, but functionally a veggie)
- Zucchini
- Cabbage
- Mushrooms
- watercress
- Cauliflower
- Brussel sprouts
Low Toxicity Fruits
When it comes to fruit, berries make the best addition to your intermittent fasting food list. They’re low-ish in sugar — most berries are less than 10% carbs by weight.
They’re also loaded with enough antioxidants to prevent the glycation that might otherwise result from their sugar content. The chart below shows just how different berries are from most other fruits.
| Nutrient | Apple (1 large) | Pear (1 medium) | Blackberries (1 cup) | Fruit Juice (200mL) |
| Fructose | 25 grams | 16 grams | 12 grams | 17 grams |
| Fiber | 5 grams | 6 grams | 13 grams | 0.7 grams |
| Antioxidants | 8% Vit. C RDA | 10% Vit. C RDA | 71% Vit. C RDA | 24% Vit. C RDA |
Blackberries, raspberries, and strawberries are among the best berries to eat during intermittent fasting.
Pair them with cream or creme fraiche for a truly tasty and nourishing fast-breaking treat.
Sample Intermittent Fasting Meal Plan
This sample intermittent fasting meal plan is an example of what two meals a day within a restricted eating window can look like over a single week.
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 | |
| Lunch | Ribeye Steak and 2 eggs Asparagus sauteed in ghee | 3 scrambled eggs with creme fraiche & ½ avocado | 80z. Lamb chops 3 Eggs ½ cup strawberries | 8 oz. Pork belly and 2 eggs with creme fraiche | Ground bison with butter and 2 eggs and ½ avocado | 4 scrambled eggs with tallow and creme fraiche Sweetpotato | 8 oz Tri-tip roast 1 medium potato baked in tallow |
| Dinner | 8 oz Tri-tip roast Sweet Potato with 1tbls ghee blackberries with 3 tablespoons of heavy cream | 8 oz bison burger ½ cup 1 kiwi | 12 oz. Beef short ribs | Ribeye steak with 2 tbls tallow and raw Oysters (3) | 6 oz. Bone marrow Asparagus sauteed in ghee | 8 oz wild salmon baked with creme fraiche 1 kiwi | 6.5 oz Bison burger with 1.5 oz liver blended in 1 Kiwi |
What to eat during intermittent fasting: the takeaway
Intermittent fasting is more than just a way of eating. It’s a way of life.
While a large part of this lifestyle’s health benefits comes from meal timing, carefully considering the best foods to eat while intermittent fasting can have an equal impact on your health and wellness goals.
Focusing on nutrient-dense whole animal foods brings intermittent fasting into an ancestral approach to eating that humans are evolved to thrive on.